A recent article by Andy Mukherjee, predicting the end of India’s IT industry has caused lot of commotion. Though, the ‘end’ is an exaggeration, the warning of the ground slipping is not new. The declining growth is owing to the rapid transformation in technology and Software Industry itself, globally.
The first Software policy of 1986, resulted into Software Technology Park (STP) scheme in 1991. Undoubtedly, the policy was highly successful with IT industry today accounting more than 9 % of GDP.
Despite diminishing growth, even after 25 years, old Software policy (1.0) of 1986 still prevails, with focus on IT services. A reworked IT policy 2012, is generic, remained redundant with no meaningful churn out for new age Industry.
Failure to capitalize on the capability built in last quarter century can have serious consequences. The onus lies with Ministry of Electronics and IT (MeitY). However, MeitY seems to be missing on following four issues.
One, Software is core, not IT enabled Services (ITeS). Two, not able to gauge the shift in fundamental industry structure globally from ‘services’ to ‘products’ and also ‘cloud’ based products. Three, not able to appreciate ‘national competitive advantage’ has moved up the maturity curve to ‘Innovation stage’. Four, a phlegmatic approach resisting shifting gears swiftly.
To address these strategic paradigm shifts, a Software 2.0 policy is needed with ‘product’ as focal to it. We are at least 5 years late in our action here. Let us delve here into the four issues and related actionable.
Software is the focal sector in IT
It is important to understand here, that the genesis of today’s IT Industry was ‘Software’. The empirical evidence highlights real horse power coming from Software. IT enabled services (ITeS) is a derivative or related sector that grew through a ‘pull through’ effect of various related determinants (R. Heeks 2006). This is true even when we cut through the industry’s maturity stages. The ‘core’ has to be energised for new paradigm.
Product focus (new paradigm)
The big sector level transformative shift is ‘Standardised Product’ taking the center stage. This cuts across the ready Software packages (small, modular or enterprise grade), SaaS, PaaS and mobile apps.
The only subtle difference which remains is, whether a ‘product’ is sold to the end-user as ‘goods’ or a ‘product’ is hosted by SaaS or PaaS producer to provision the ‘productised service’. Even IT services business now hinges at standardised ‘products’ for revenues.
Shifting National Competitive advantage
For about a decade no one believed that Software policy 1.0 could make India a super star in Software sector. It is only after about a decade, researchers recognized that India, a developing country could become a follower nation in Software sector. This was in sharp contrast to other 2 rising countries in same period of late 1980s i.e. Israel and Ireland, who were ascribed as Industrialized nation by world bank even in that period among the 3Is.
Usually academic researchers have not been very successful in predicting or prescribing favourable industrial policy for a country. But, they have played an important role when we apply an established research for analysing a sector’s performance and understanding the needed strategic shift.
Also, the classical economics models of ‘comparative advantage’ do not fit well for a sector like Software which is replete with advanced factor conditions.
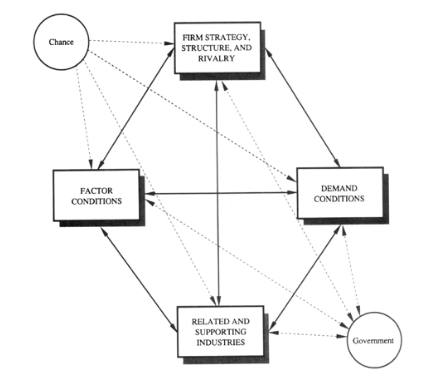
The most comprehensive model to deep delve into this search is Michael Porter’s theory of competitive advantage (The Competitive Advantage of Nations, 1990). It goes beyond the macroeconomic theories on competitiveness and also incorporates the aspects of business and industry with advanced factors such as technology & innovation. The “diamond” model is based on four main determinant categories viz. factor conditions, demand conditions, Related and Supporting Industries and Firm Strategy, Structure, and Rivalry. It also incorporates and interlinks two extra parameters of a) chance and b) Government policy. For India both these played a vital role.
Porter’s Diamond Model. Source: The Competitive Advantage of Nations, 1990, Michael Porter’s (Kindle book, position 3060)
The national competitive advantage is based on the advanced level interplay of these determinants in the above diamond, network.
The model may lack in taking into account the new emerging factors of cloud and mobility computing. Yet, it offers a comprehensive and advanced postulation that can help understand the sectoral impacts.
Richard Heeks (2006), using this model concluded the competitiveness of Software sector of India. So also Bhattacharjee and Chakraborty (2015), further building on Heeks study. Richard Heeks (2006) says, “full diamond is not (yet) in place”. Whereas Bhattacharjee and Chakraborty (2015), recognize the full diamond in place. (Please see reference below at bottom)
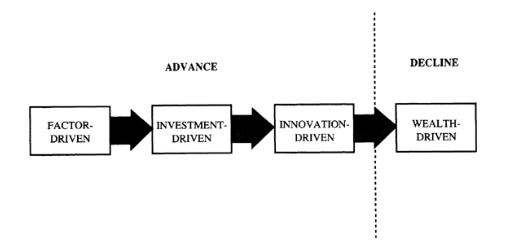
Going beyond famous diamond model, the stages of development as postulated by Porter are more relevant to understand our readiness for ‘product’ stage. The stages in order are ‘factor driven’, ‘investment driven’ and ‘innovation driven’ (the last wealth creation points decline). R. Heeks (2006) finds ‘Investment driven’ stage in 2006. Bhattacharjee and Chakraborty finds ‘innovation’ having swept in the period 2012-2015.
Stages of development. Source: The Competitive Advantage of Nations, 1990, Michael Porter’s from kindle book location 9634
“Govt. helping improve the quality of domestic demand and encouraging local startups” is representative of ‘innovation’ stage, says Heeks (2006). One can easily map here, the conditions arising to launch of StartupIndia policy 2015 and other accompanying developments.
Yet another symptom of ‘innovation driven’ stage is the domestic demand conditions undergoing a rapid change. ‘Digital India’, GST and UPI are not only concurrent, country scale demand generation programs, but also innovation boosters in domestic industry.
Porters, argues for a proactive role for cluster in National competitive advantage. The clusters enable innovation and speed productivity growth. The Silicon Valley and Israel’s Silicon Wadi are clusters that contribute to regional growth as well as making them as global brand. India has a distributed cluster model spread across various Tier 1, Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities. Bangalore, Hyderabad, Pune, Delhi NCR and Chennai being prominent.
India has enriched these clusters in the investment phase recognized by both the referred researches above.
In India, a mass of new age Software product startups has emerged touching wide array of industries. Advanced and specialized factor resources are emanating from the Software product development happening in the captive offshore center, R&D centers of MNCs or by outsourced product development (OPD) vendors, across all major IT cluster in country.
India therefore is poised for a phase 2 of Software Industry this time with product focus.
Emerging SaaS segment has global reach
SaaS can be the next game changer for India. The national competitive advantage can be capitalized for creating a SaaS industry, and puts India in first three slot on global map.
Many Software as a Service (SaaS) companies like Zoho, Freshdesk are already global market place names, pitching for leadership in their own segments. It proves the power of SaaS to give edge in exports.
Out of more than 200 SaaS companies, number of them have incorporated outside, owing to the friction in doing global business from India. Software 1.0 policy doesn’t care for their issues. This loss can be plugged with Software 2.0.
Swift action needed by Government
India’s IT sector is strong enough to face changing technology challenges. It needs a ‘product nation’ based proactive strategy, that deals with ‘product ecosystem’ development, R&D, domestic demand boosters, frictionless trade and tax regime.
MeitY should rise to the occasion and announce a macro level policy framework, without wasting further time. Action plans (schemes, programs, incentives and institutional setups) can follow on need basis and in phased manner. This is how it happened in Software 1.0 policy as well. A new institutional setup is required. ‘National Software Product Mission’ should be setup urgently to cater to emerging Software product industry.
‘Software product power’ is cardinal to retaining global Software ‘power’ tag. Globally Software product market is estimated to be $1.2 trillion by 2025. India needs to target for 10-15 % of this. At home front, India needs to create ~3.5 million new jobs by 2025. Choices are limited.
iSPIRT has been working with MeitY for last 2 years to persuade them for taking a stand for a national level product industry while the service industry keeps growing. A nine point strategy draft is under consideration. But it has taken lot of time. In hardware product space, we have National Electronic Policy 2012. A National Policy on Software Product will replenish the industrial policy basket of MeitY and usher in growth in new areas of both domestic and international trade.
“Mere incremental progress is not enough. A metamorphosis is needed. That is why my vision for India is rapid transformation, not gradual evolution”, said Prime Minister at NITI Aayog recently.
We hope the announcement of the long pending ‘National Policy on Software Product’ (NPSP) will soon be forthcoming. Only then will PM’s dream of rapid transformation, become a reality to catalyze an “Indian Software 2.0 industry”.
Main References used
1. Research article “Using Competitive Advantage Theory to Analyze IT Sectors in Developing Countries: A Software Industry Case Analysis”. By Richard Heeks, Development Informatics Group Institute for Development Policy and Management School of Environment and Development University of Manchester, Manchester, United Kingdom. http://itidjournal.org/itid/article/viewFile/228/98
2. Research paper, “Investigating India’s competitive edge in the IT-ITeS sector”. By Sankalpa Bhattacharjee and Debkumar Chakrabarti (Peer-review under responsibility of Indian Institute of Management Bangalore). http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S097038961500004X
3. The Competitive Advantage of Nations, by Michael E. Porter’s Free Press edition 1990