India currently has 90 unicorns – startup companies that are valued at over $1b – and will likely soon have 100 unicorns, becoming the third such country after the USA and China. Since January 2016 when the “Startup India” program was launched, the startup ecosystem of India including infrastructure for startups, be it incubators, mentorship, funding, corporate initiatives, media coverage, or even patent filing, has improved substantially making life easier for entrepreneurs.
However, it is still not as smooth a ride for the Indian start-ups as it is for startups in the advanced economies of say, the USA, Singapore, and China. Our “ease of doing business” is yet to be on par with the developed world, especially given the high taxation, onerous compliance requirements, inadequate and cumbersome legal protection of IP, as well as time-consuming and expensive processes to access capital and secure exits. It isn’t a surprise therefore that many companies are shifting their primary legal location to foreign jurisdictions like the USA, and Singapore.
How do the numbers stand?
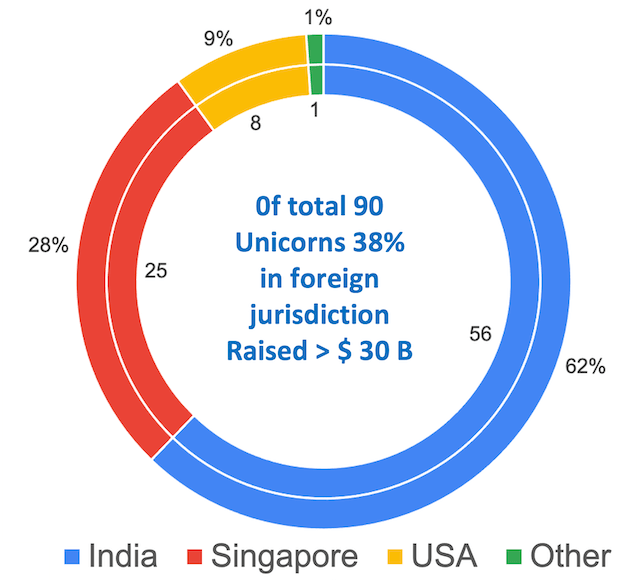
As per a study by Venture Intelligence, of the presently known 90 “Indian” unicorns), 56 are based in India, 25 in the USA, 8 in Singapore, and 1 in the Netherlands spanning sectors from e-Commerce to fintech to gaming and more. In other words, 38% of “Indian” unicorns are not quite Indian as they are domiciled outside of India. Moreover, these 34 unicorns have raised approximately $30B ie, this large money could have been but hasn’t been invested into an India domiciled entity.
Sector Wise break-up of the Unicorns
Chart: Sector-wise domicile of unicorns as on 31st March 2022.
The reasons for incorporating in the USA are different from incorporating in say, Singapore. SaaS founders find it easier to reach out to the large market for SaaS “Software as a Service” based offerings in the USA by incorporating there. Companies incorporated in Singapore for high “ease of doing business”, low taxation, quality infrastructure, and quality of life while remaining close to India.
Out of 12 Indian unicorns in the SaaS category, all except Zoho and Darwinbox are based in the USA. SaaS offerings are expected to be a $1 trillion opportunity and India will lose wealth creation, tax revenues, listing, and related income, by not having these companies domiciled in India.
Of the three unicorns in a frontier technology area like Artificial Intelligence, namely – Glance, Fractal, and Mindtickle, one is registered in Singapore while the other two are in the USA. Of the 3 unicorns in Gaming, Mobile Premier League and Dream 11 are based in Singapore and New Jersey respectively while Games 24×7 is registered in India.
Flipkart, India’s greatest startup success story and the poster boy for Indian e-commerce, which was acquired by Walmart at a valuation of over $20B, was domiciled in Singapore. That set the trend of e-commerce companies having their HQs in the island country. There are many Singapore shell companies set up by VC funds to become holding companies for Indian subsidiaries. Singapore is today the hottest destination for the registration of Indian e-commerce players.
Even more worrying than this trend of registering the parent company outside India is the migration of startup founders to UAE and Singapore. Lower taxes, easier access to capital, government support, simple compliance, and better quality of life while being just a short flight away from India make the UAE and Singapore rather attractive to founders.
Whichever country our startups chose to register or our founders chose to migrate to, the ultimate loser is India with intellectual property ownership and funds being vested in non-Indian jurisdictions.
Stay in India Mission
In order to retain the economic value added by the start-up ecosystem, it is important that India urgently puts in place policies that ensure that founders and startups ‘Stay-in-India”. This will require the coming together of various ministries, particularly DPIIT/Min of Commerce, Ministry of Finance, Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology, and regulators like the Reserve Bank of India and Securities and Exchange Board of India to address the Stay-in-India Checklist.
Stay-in-India is an evolving checklist of issues that need to be solved to contain the exodus of startups from India. These issues fall under four categories: a) Ease of doing business and making it easy to raise funds; b) harmonization of coding of digital economy c) Reducing overall tax anomalies and d) Increased DTA and foreign markets access.
The issues are comprehensively listed in the Stay-in-India checklist.
As an example, let’s consider the anomalies in the taxation of dividends. Dividend received from overseas subsidiaries, that has been already taxed, is taxed once again in India as income in the hands of the company. Also, while the rate of tax on such dividends for certain companies is 15% (as against 30%), the same exemption is not provided to limited-liability partnerships and individuals. It amounts to double taxation of income and discourages a model where overseas subsidiaries of Indian startups can pay dividends at lower tax rates to Indian shareholders. Removal of this dividend tax will directly encourage start-ups to remain domiciled in India and receive dividend income from subsidiaries abroad.
Similarly, there are regulatory frictions e.g. TDS on the sale of software products which reduces the working capital in hands of Software product companies, or the need for filling the Softex form (which was relevant in the early days of IT services exports), and which is now redundant as GSTN Invoices already have the required and sufficient data. All that is required is for different departments of the Govt and regulators to connect digitally and share information. The unfavourable tax regime for IPR protection, such as subjection to minimum alternate tax, IPRs being subject to income tax, and not capital gains even when they are held for more than a year is another big irritant. Technology-heavy startups, therefore, tend to relocate to jurisdictions like Singapore and the USA that have a smoother and lower-cost approach. Founders relocating to overseas jurisdictions are typically seen around the time of M&A. One of the reasons relates to taxation: typically, a portion of the financial proceeds arising from an M&A transaction is held in escrow and released to the founders after some time and/or completion of certain contractual obligations. The escrow payments are treated as income by the Indian tax authorities rather than capital gains as other jurisdictions do – this needs resolution.
India is emerging as a global startup hub, with the support of the Govt, with our startups attracting capital and talent while being at the forefront of innovation, jobs, wealth, and intellectual property creation. Brand India is enhanced globally by the success of Indian startups. With more support from the Government by way of removal of regulatory friction and by providing incentives – fiscal and regulatory – the ecosystem required to create, enable and grow Indian startups will dramatically accelerate.
The Ease of Doing Business must be tackled in mission mode with the Stay-in-India Mission (SIIM) being an integral part of India is to secure its rightful place around the global innovation table.
The blog post is co-authored by our volunteers Sanjay Anandram and Amit Agrahari. You can reach out to Amit at [email protected]
Disclaimer: The article depends upon various pubic data sources apart from credible data sources that are relevant at the current date and time. Readers may like to read this accordingly.
Data Sources Courtesy: 1. Venture Intelligence. 2. Invest India

