NASA.GE. Disney. A global software product – Kayako. Jalandhar – a growing city in Punjab,India. And a school kid who opted out of University. Sounds like the script of the next “The Social Network” hollywood movie. The truth – the movie might have to wait. Because this success story from India’s hinterland is only getting started.
And yes the school kid who was only seventeen in 2001 at the time of launching this enterprise helpdesk product is still leading from the front as the Founder and CEO.
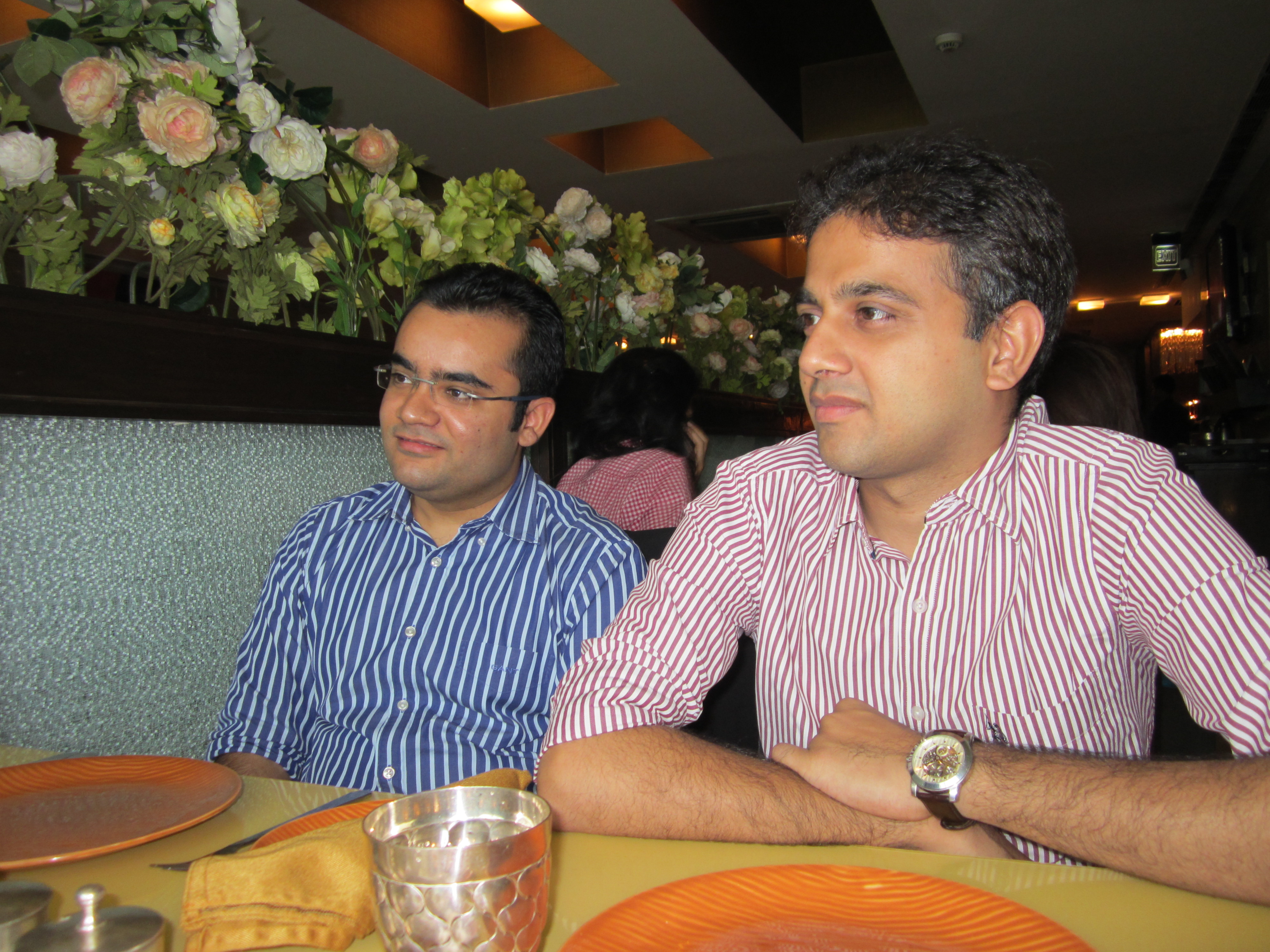
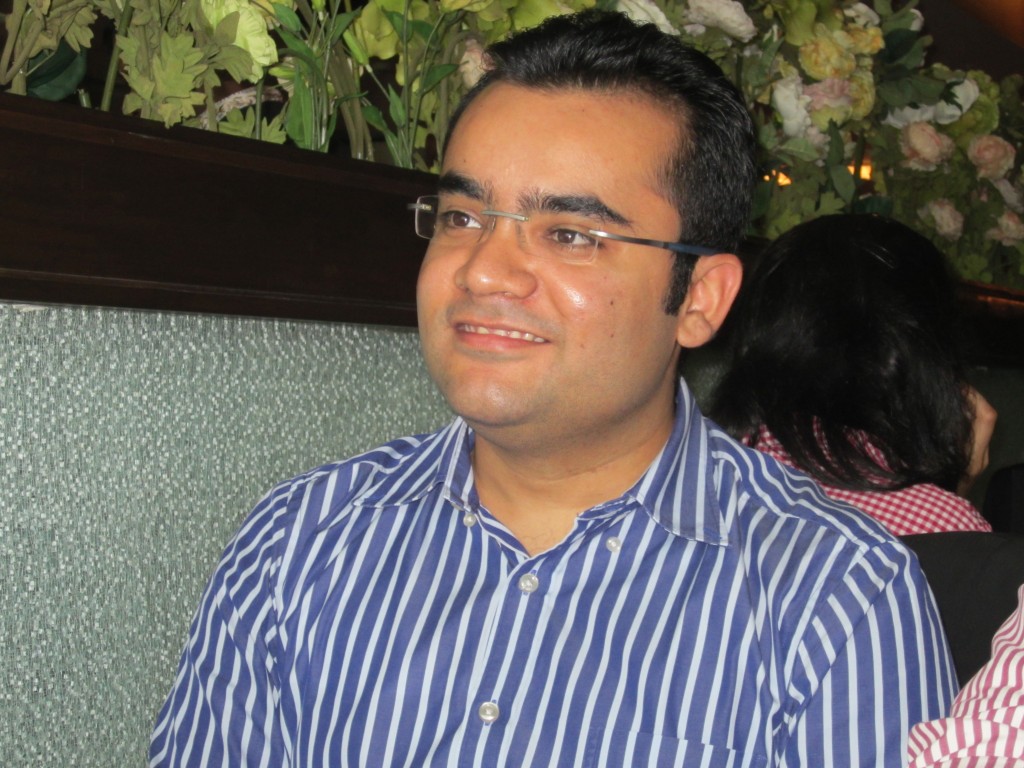
ProductNation is excited to bring to you this riveting story through a heart-to-heart talk with Mr Varun Shoor. A lunch interview was quickly planned and Varun suggested “Punjabi By Nature” at Cyber City Gurgaon.
On interview day, we met at Varun’s swanky 16th floor office at Cyber City Gurgaon that houses the product engineering team. RFID check-ins, Apple Machines, top of the line interiors, extensive use of glass and a panoramic view of Gurgaon would be some add-ons if you consider employment opportunities here. After exchanging pleasantries and a quick discussion on the quirky weather, we did a quick jaunt across the road to the “Punjabi By Nature” restaurant.
Raghav Arora – Varun’s schoolmate and core member of the Management team also joined in. A quick scan of the Menu slate (yes, it is a wooden slate) and we were sorted with our orders. It was time. 1-2-3 Action!

ProductNation: So Varun, we are eager to listen to your story.
Varun Shoor: Right from childhood, I was a geeky kid. None of my sister’s electronic dogs survived the second day. My dad felt that if I went to a hostel, some sense would dawn on me.
At the hostel, I saw computers for the first time. 286, DOS, monochromatic display and there I learnt the programming language LOGO where in you draw shapes by issuing commands. That was fascinating. The first four years in hostel, I used to hungrily look forward to the Computer Class each day and excelled with 90% marks.
After I came back from hostel I asked dad for a computer. This was 1996. Fortunately, my dad could afford one. It was a Packard Bell 286 with Windows 3.1.
Back then there was no internet in Jalandhar, only in Delhi and metros. Luckily there was a cyber café in Jalandhar which used to dial out to Delhi. I used it to look up the latest apps, download them. Fascinating it was, especially the noise of dial up and Rs 15 per minute internet charge.
We all burst into a nostalgic laughter. If you are wondering why, then your association with the Internet is at best recent.
ProductNation: Please continue
Varun Shoor: Sabeer Bhatia then had sold off Hotmail. That was when I decided to start a web design firm – Cyfox Graphics – using Dad’s card to buy a domain name – domains were US $ 100 then and web hosting. But as I devoted more time to computers, academics went down and long distance STD call bills were going up. One day, an internet bill of Rs Rs 60,000 greeted my family. Promptly, Dad took away the credit card. That dream was over.
Studies was tough. In Class VIII, I was conditionally promoted. And in class IX, I was kicked out as I had just 39%. From the beginning though I was not good in studies, I was a bookworm. I always knew more than the teachers. But, I was never good in cramming for the exams.
Parallely, I did couple of websites and a solution called Shoutbox service that provided chat rooms on websites where visitors could enter. This became popular but I could not pay for the server. Then I came up with a service called Deskpost that was like hotscripts, a script directory.
Since I was into web hosting, I used to be active on a web hosting forum called Web Hosting Talk. I saw people buying a service called Wonderdesk at US $2000. I made something similar called Active Support and wanted to try selling it.
For that I needed three things – domain, hosting and credit card processing. So I went to dad and no guesses for what he told me. So here I am, with a product but no resources.
 So I went into IRC chat rooms asking for a domain I could use. I was banned but I kept trying with proxys. Finally one guy reverts saying he has two domain names – kayako.com and akimbomedia.com. You know what happened next.
So I went into IRC chat rooms asking for a domain I could use. I was banned but I kept trying with proxys. Finally one guy reverts saying he has two domain names – kayako.com and akimbomedia.com. You know what happened next.
Then I needed hosting. My friend in Jalandhar agreed on the condition that I would pay him in six months.
Last was a credit card processing tool. I wanted Tool Check Out. It is still very popular. It came for US $ 50. Where do I get US $ 50? I go back to the chat rooms announcing that I will give a US $ 2000 product for US $ 50. And I didn’t need the money, just the Tool Check Out account. So again banned, kicked out of forums.
Then a guy who runs a hosting company becomes interested and transfers the Tool Check Out account to my name. Then I create a website and launch the product. Version 1 comes into picture.
Money accumulates to US $2000 which is the minimum withdrawal threshold for Tool CheckOut. I wire that money to a friend’s account and ask him to ship a Compaq Laptop to me. I tell my dad that I have bought a laptop and it would reach in a week’s time.
A week, no laptop. Two weeks, no laptop. Three weeks, no laptop. Every day I am asking about the laptop parcel and dad was pretty irritated. On a positive note, the money started accumulating again. I tell my dad, I have US $2000 and please give me your bank details and I will wire it. Reluctantly lest I hack his account, he gave me the bank details.
So I take the details and tell mom and dad that by next Thursday they would see a wire transfer of US $2000. Thursday is here, but no money. Friday, no money. And I am pestering them every hour if there is any credit. They were sick by then.
Come Monday. Since I used to work in the night, I was sleeping when my Mom jolts me out of my slumber in the afternoon. She says – “paise aa gaye, paise aa gaye, tu jhooth nahin bol raha tha” (The money is here, money is here, you were not lying). And I say – “I was always telling the truth. You never believed me”.
The very next day, the Laptop arrives. And that was how the company began. No money, no nothing and we started this company. Closer to Class XII, I told my father that I did not want to go to college and wanted to do Kayako for life. My Dad having heard about Sabeer Bhatia stories encouraged me to go ahead.
And we started Kayako in November 2001.
By that time, the Raan and the Tikkis had soaked the story enough to be guided to their rightful destination. The Raan was sliced just right to whet our appetite even further. Yeah, it is highly recommended.
ProductNation: Very interesting. When you were setting up Kayako, companies like Infosys, Wipro were playing the IT services card. Did you ever contemplate that?
Varun Shoor: I am an introvert who was forced to become an extrovert. And I did not have it in me to meet clients, convince people, sell something. So services were out of the question. Secondly, I was enjoying what I was doing.
The Raan was just awesome. There was no need to outdo it. So, the simple fare of yellow dal and makhni murg with Naan that followed was just right.
ProductNation: Nowadays, IT entrepreneurs in India are focused more on products and not services. What would be your message to them?
Varun Shoor: First, do not chase money. If you do, you will lose focus. Second, your product has to have a VOW factor. It has to be awesome, period.
Third, start building around things that actually generate sales – a good website and a strong trust factor. How do you do that? Testimonials, client portfolio, live chat, updated news feed, active social media accounts, phone number on the site answered and engaging plus trusting website copy. Last, Think global, thing Big. Then your standards go up and your market has no limitations. And this also cushions you against business cycles.
Product Nation: Where do you want to see Kayako in next 3 – 5 years? How do you want to position Kayako?
Varun Shoor: Honestly, we are going with the flow. We are trying to be better than yesterday. Where this takes us, we have no idea. On positioning, we are focused completely on the product. On what really matters. Making sure each of our customers is happy. We are passionate about support and helpdesk. And we want to continue with our sharp focus on that.
It was time to focus on the desserts now. So it was a sinful hot chocolate fudge for Varun and Gulab Jamuns – the size of golf balls – for Raghav and us. A quick check out and we were out into the hustle bustle of Cyber City Gurgaon.
We then ask Varun – “What is the next opportunity you would like to pursue?” Without batting an eye lid, he responds – “A Five Star hotel”. And adds. “I like change and I am fascinated by architecture. And if I find something interesting in IT, I could take that up as well.”
And as we prepare to bid good bye, he says, “We are planning a strong initiative that we intend to go live in March next year. So watch out”.
Good Luck, Kayako!
 There has been an acceleration since 2010 in the pace of creation of B2B companies. Vertically-focused offerings in retail, travel, financial services, media have reached scale and we are likely to see some larger exits in terms of IPOs or M&A over the next couple of years. In parallel, we are seeing horizontal offerings targeting global markets emerge and start to breakout of India into the US and other global markets – we are starting to see not only India-based venture funds backing these companies but also Silicon Valley funds coming in once there is initial customer adoption in the US.
There has been an acceleration since 2010 in the pace of creation of B2B companies. Vertically-focused offerings in retail, travel, financial services, media have reached scale and we are likely to see some larger exits in terms of IPOs or M&A over the next couple of years. In parallel, we are seeing horizontal offerings targeting global markets emerge and start to breakout of India into the US and other global markets – we are starting to see not only India-based venture funds backing these companies but also Silicon Valley funds coming in once there is initial customer adoption in the US.