I’m forever being asked a question by the people I meet during my travels, events, etc. I usually smile and avoid it. Or let someone embarrass me by talking about how important and selfless my work has been and is being. But I’ve never really tackled that question on my own. Perhaps I needed to think about it myself. A few days ago, when I was looking back at three years of Playbooks, the action-focussed Product Nation workshops that we conduct, and of course other events, it got me thinking. It was probably time to face that question myself, and answer it, if not for other people, then at least for myself.
When we started iSPIRT, no real sense of a product community existed in India. People in several corners of our vast country were building great products and companies, but there was no attempt at coherence, no communication channel that existed that could make them way more than the sum of the parts. This was why we began the journey of iSPIRT; we wanted to build this community that would add real value to founders; we wanted to help the guy in the mud pit, or as Roosevelt called him, ‘the man in the arena daring greatly”’. And yet, we did not want to be facilitators of any sort. We wanted to be there with the entrepreneur through the long, hard road. We wanted to be the people he could always rely on. We wanted to go deeper.
And this thinking was what led us eventually to the entrepreneur who was in the stage Sharad Sharma termed ‘happy-confused’. This was the Sharad came up with for the entrepreneur who’s found his market, has figured out how to sell his product, but is now stalled at a stage when he doesn’t understand how to go further. In other words, the question of scale. Should he pursue scale? If so, how? It was this guy who needed help, and perhaps some direction, from the people who had already done it before.
So we began a series of programs and bootcamps that in hindsight, look and feel like a lot, but which at the time were just great fun to put together. I’ll give you a small brief on each of them; they have been some of the most interesting initiatives that i have got to work on in the last 3 years.

The Playbooks
The Playbook RoundTables, started off with a conversation which had Vivek Subramanyam (Fintellix), Aneesh Reddy (Capillary), Ashish Gupta (Helion) and Sharad (the i of iSPIRT!). After a few brainstorming sessions, the format was decided: It would be a gathering of 12 like-minded product startups(curated) who are beyond the early stage. These RoundTable will be facilitated by an in-the-saddle entrepreneur (we called them iSPIRT Mavens) who is well accomplished on a particular topic/theme. Shankar Maruwada (EkStep) opened the innings for us, and the participants were blown away by the way Shankar conducted the RT. A lot of the success of the Playbooks was because of that first session, which set the tone for them. Pallav Nadhani (FusionCharts) was one of the participants and he added lot of his insights in the RT. We were then joined by Aneesh Reddy, Sridhar Ranganathan, Samir Palnitkar, Amit Ranjan and Amit Somani who helped us with the early RTs. There was so much preparation that would go into the Playbooks – identifying the right audience, the seating, when should we take a break, how do we get the feedback, ensure it’s free of bias, how do we measure (NPS!) and improve upon it? Until today, in every PlaybookRT, we’ve measured the NPS and continue to incorporate it into program decisions.

The First Product Bootcamp #PNcamp
As the Playbook Roundtables became popular, we had the idea wanted to do something at a slightly bigger scale and bring more product founders together. Just the idea caused us excitement enough to push ahead. We started off by calling it PNSummit and then the name changed to PNCamp. We had some of our best volunteers working on this one and Rajan (as always) drove us crazy with different types of organising calls (a war room, a morning huddle, an evening huddle, etc). We explored many formats for PNcamp and then conducted many RTs for different audiences (Discovery/Scale stage) to figure out the best way to do it. I think this was one of the best bootcamps I was part of. It took us such a lot of effort to put this together that we never attempted to do this again. I hope someone from Pune will take the lead and do this for us. We have a blueprint and with few volunteers, we can pull this together again!

The people who make magic happen – Mavens, Volunteers & Friends
The Mavens have played an important role in making the magic happen for the Playbooks. Most of the mavens get naked (metaphorically) with the audience and share many of their hard-won experiences openly. It’s really great to see some of the rock-solid CEOs passionately help each other. I get many volunteers who reach out to me and want to help me in putting together these roundtables, but the fact is very few of them can put in the effort into making such magic happen. From the outside it looks very simple, but it takes lot of effort in curating the event, inviting the right people and then closing the feedback. I’m grateful to the mavens, the volunteers and people like Rajan & Sharad who have always been supportive in making the magic happen again & again.

Playbooks: New Formats
We slowed down on the Playbooks a bit after that, as I got busy with many other things in iSPIRT, including a policy push. We also tried a few experiments with some mavens, but none of the other formats came good. We maintained the rule of never inviting someone to do a Playbook without them having attended one. We have stayed away from getting some of the Gurus who want to just give gyaan. We are still happy to explore new formats which can help product founders. I recently stumbled upon the Product Tear Down session at SaaSx and I think if we can do this right, this can become a great platform for product founders who are looking for help.
SaaSx
On one of my visits to Chennai, I realised that some of the SaaS leaders are based out of the city and there is no platform for all of them to come together. After few conversations with Suresh Sambandam // KissFlow (the marketer), who at that time had just returned after attending SaaStr. He was blown away by the energy and kind of conversations that took place at the conference. We started putting something together; Suresh coined the name SaaSx and with help from leaders like Shekhar Kirani (Accel), Girish Mathrubootham (Freshdesk), Paras Chopra (Wingify), Avlesh Singh (WebEngage), we launched the first edition and it was a big hit. We reached out to folks and almost everyone wanted SaaSx to be held twice a year. We actually had kept it very light; it did not take more time for us to get it up. We always have been able to put up SaaSx in 3-4 weeks. The recent edition was amazing in terms of content and curation, and the networking that it created. It was good to catch up with lots of founders who always seem to appreciate me for events like this, though I’ve always believed that the real rockstars are the volunteers who pull this together.

PNgrowth
This one was special. It happened over a long passionate conversation on Category Leadership with Pallav. We did several meetings, and calls with the Stanford/Duke & the iSPIRT Playbook team, and it took approximately 9 months for PNgrowth to take birth :). Rajan & I were nervous till the end, but I think the format and some of the conversations/talks by Shankar, Pallav, Sharad, Kunal, Nags, and Aneesh made all the difference. I think the best part for me was the bonding amongst the founders. We had around 186 founders who attended, many of them took back some great insights, learnings, some made great friends and I think we created a new platform. Hopefully, we can build on this and take it forward.

Returning to that question
To be yourself in a world that is constantly trying to make you something else is the greatest accomplishment ~Ralph Waldo Emerson.
And so we return to the question I began this rather long post with. In a recent session with the founders, Pallav again asked me why I’m so passionate about the ecosystem and why I continue to all all this evangelising. And I couldn’t push it away anymore. It made me think question my own motivations, and I came up with something like an answer.
So here we go –
- I think of myself as a connector, and since I have been in the ecosystem for a long time, I know many smart people who will benefit by being introduced to other smart people. I’m able to do that, and that makes me happy. I do this without expecting anything in return. There are a few other connectors in our ecosystem who selflessly do this, and they should be celebrated as well.
- After evangelising the Product Eco-system for over 12 years, I really want some Indian product companies to go global, to become category leaders. We have had some success in the past, but I would love it if many more would rise from India, and we truly become a ProductNation. I consider myself lucky to be working with some of the smartest people in the ecosystem.
- We have many founders who are believers in the Pay-It-Forward movement, but they want to find credible platforms to associate with. Fortunately, iSPIRT has become one of those platforms where they consider opening up and helping other product founders
- I stay away from the limelight as it defocuses you. You tend to go after visibility and lose focus. Long time back i had heard this saying if you make a donation, don’t publicise it. Let it just be a donation. I don’t know if that is right or wrong, but that’s what I follow.
- I love my work as I get to meet lot of people, make new friends and build deeper relationships with the existing ones.
I think that’s all there is to it. 🙂
How can you support the movement?
I get lot of emails, lots of calls and lot of people reach out to me at conferences saying that they would like to volunteer. Many times, people are not clear on what their strengths are and don’t even know how they can contribute. Volunteering is not easy. I would request people to read the iSPIRT website, see the kind of activities being done and think how would you like to contribute. Then write to us. If you don’t show the passion, it’s hard for us to make you part of this movement. But if you do, and become part of this movement, I’m sure you’ll enjoy every bit of this ride we are on – to make India a true Product Nation.
Thanks to Sairam for helping in editing this blog post.







 “A great product manager has the brain of an engineer, the heart of a designer, and the speech of a diplomat”
“A great product manager has the brain of an engineer, the heart of a designer, and the speech of a diplomat” Amit emphasised the importance of tracking the product’s viral coefficient which is the number of additional members every new member brings. It should be greater than 1 for the product to become viral.
Amit emphasised the importance of tracking the product’s viral coefficient which is the number of additional members every new member brings. It should be greater than 1 for the product to become viral.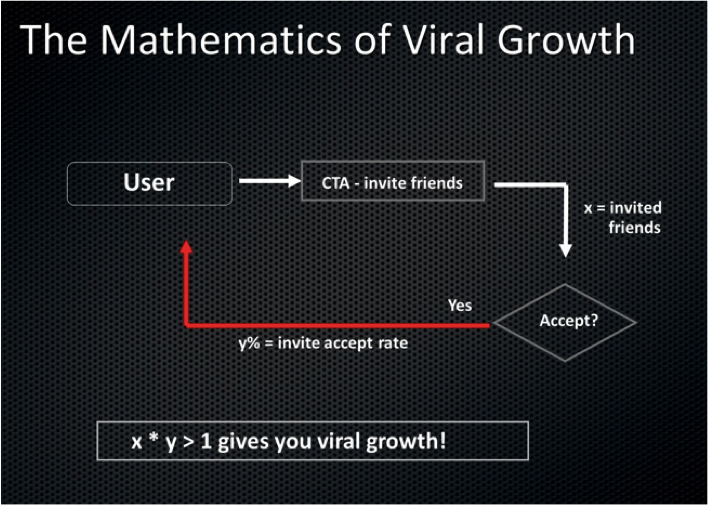
 Overview
Overview Digital vs. Feet on Street
Digital vs. Feet on Street Monopolistic Market
Monopolistic Market The high level of interest and engagement from all participants was evident as the session that planned for 3-4 hours got extended to beyond 7 hours. We finally concluded our first Roundtable for 2015 with a promise from Deepak that he will back with us in a couple of months.
The high level of interest and engagement from all participants was evident as the session that planned for 3-4 hours got extended to beyond 7 hours. We finally concluded our first Roundtable for 2015 with a promise from Deepak that he will back with us in a couple of months. To give you a taste of how things play out in the real world:
To give you a taste of how things play out in the real world:
 Best Practices For Product Development:
Best Practices For Product Development: