This is a two part blog series. The following is the second part.
In Part 1, we traced how data collaborations are being reimagined, and laid out the conceptual foundations. From redefining consent through the Account Aggregator framework, to recognizing the limits of consent. We explored how privacy-preserving frameworks like differential privacy protect individuals even when models are built from data; how electronic contracts replace slow, manual agreements with enforceable digital rules; and how confidential clean rooms combine secure hardware and privacy guarantees to enable computation without revealing raw data.
In Part 2, we explore how these building blocks come together in practice.
The Connective Tissue: Data Collabs
Technology alone cannot guarantee privacy, fairness, or effective collaboration. Data-sharing ecosystems need institutional scaffolding — entities that can operationalize trust, manage relationships, and abstract away complexity for participants.
This is where Data Collaboratives (or Data Collabs for short) come in.
A Data Collab isn’t a regulator or a government body. Rather, it is a facilitator organization — a neutral yet entrepreneurial entity that enables, orchestrates, and sustains data collaborations using the DEPA Framework behind the scenes, following its standards and processes set by trusted bodies like an Self-Regulatory Organization (SRO) and a Technology Standards Organization (TSO).
You can think of a Data Collab as the connective tissue of a data ecosystem — linking data providers, data consumers, and service providers.
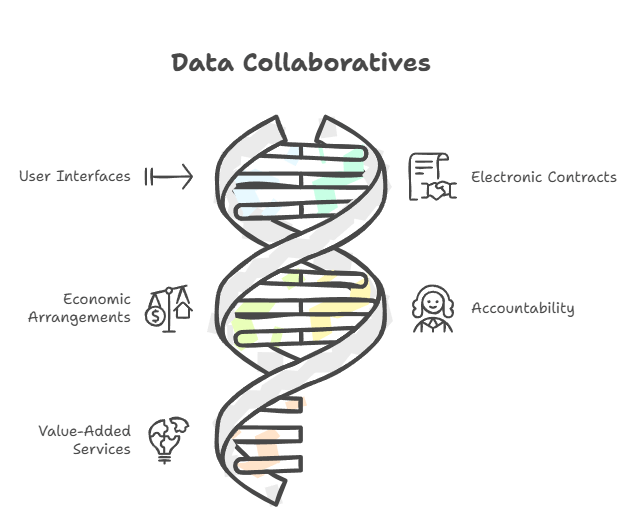
In practice, a Data Collab:
- Provides tools and interfaces for participants to register, onboard, sign electronic contracts, and set up secure collaboration environments such as CCRs.
- Signs agreements with data providers to clean, prepare, and catalogue datasets so that they can be safely shared with authorized data consumers.
- Manages the flow of value — usually collecting payments from data consumers and distributing them fairly to data providers, while covering operational costs.
- Assumes accountability for ensuring that all interactions, permissions, and computations are compliant with the DEPA rules and contractual terms.
- Adds value beyond infrastructure — offering domain expertise, workflow design, governance and audit support — streamlining data collaborations.
Data Collabs will likely take different forms depending on the domain they serve. For example, some might focus on oncology research, others on financial fraud detection or climate-risk modeling. Each field has its own kinds of data, privacy rules, and ways of working — so it is natural for Data Collabs to specialize.
Because running these collaborations requires significant operational and technical effort, most Data Collabs will probably be for-profit enterprises. At the same time, because they operate on open, interoperable digital public infrastructure like DEPA, they are not monopolistic platforms. Instead, they enable a competitive marketplace where multiple Data Collabs can coexist, offering participants better choices, fairer pricing, and higher-quality services.
In this way, Data Collabs create a persistent institutional layer for responsible data use; enabling long-term, multi-party cooperation that would be impractical to coordinate through ad hoc agreements.
A real-world example: Accelerating Drug Discovery
Imagine three pharmaceutical companies, each developing treatments for the same rare disease. Each has conducted clinical trials with a few hundred patients — but individually, none has enough data in quantity, diversity, or parameter richness to train a robust predictive model of treatment response.
Much like pieces of a puzzle, valuable insights often emerge only when data from different sources fit together — yet no single party should hold or see the entire picture.
If these companies could combine their datasets, and enrich them with other sources like gene expression profiles, cell imaging results, or public molecular databases, they could uncover deeper patterns and dramatically speed up drug discovery.
But three major barriers stand in their way:
- Competitive concerns: Each company treats its clinical data as proprietary and doesn’t want to reveal it to others.
- Privacy regulations: Patients gave consent only to the company that ran their trial — not to share data across firms.
- Practical limits: Many patients can’t be re-contacted to renew consent, making manual legal processes infeasible.
This is where the DEPA Framework fits in. Here’s how it would work:
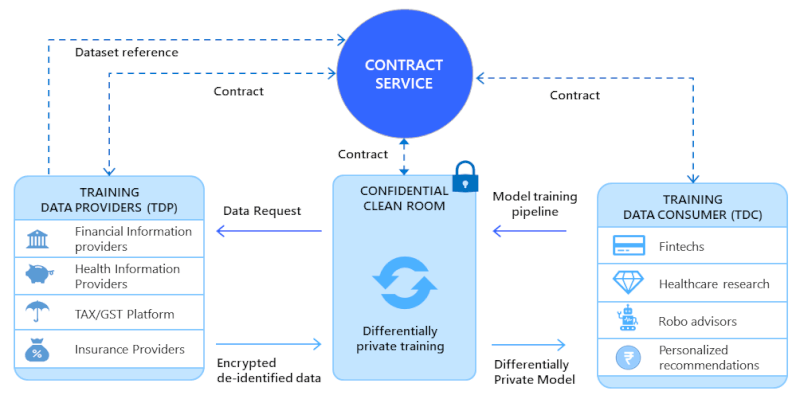
A Data Collab is formed for long-term drug discovery collaborations. It signs electronic contracts with each company, defining rights, responsibilities, and permitted use of data. It handles registration, onboarding, and compliance checks through standardized interfaces.
Electronic contracts set out the exact terms of collaboration — specifying each party’s role, the artefacts they contribute, and the rules that govern privacy, usage, and value-sharing.
Each company uploads its encrypted trial data or model into a Confidential Clean Room. Data inside the CCR is decrypted only after checks confirm that all security and compliance conditions are met.
Data is programmatically joined and enriched within the CCR, followed by AI model training using privacy-enhancing techniques like differential privacy, which appropriately bound the chance of re-identifying patients.
Only the final trained model and its accompanying logs — never the underlying data — leave the CCR. The model can be decrypted solely by the authorized data consumer(s) (i.e. the modellers), protecting their trade secrets.
Auditors can review logs and trace the provenance of all artefacts at any time — via the DEPA AI Chain — to verify compliance and resolve disputes.
This framework delivers several benefits for all concerned stakeholders:
- For society: Promising treatments reach patients faster, while a reusable governance and technology blueprint emerges for future biomedical collaborations.
- For the economy: A new data-driven economy is unlocked, enabling novel business interactions and boosting meaningful economic activity.
- For companies: They can innovate together without exposing trade secrets or breaking regulatory rules, expanding what’s possible in research and development.
- For regulators and auditors: Every transaction leaves a verifiable trail, simplifying oversight and boosting trust in the ecosystem.
Summing up
India’s journey toward responsible data use has been progressive and layered.
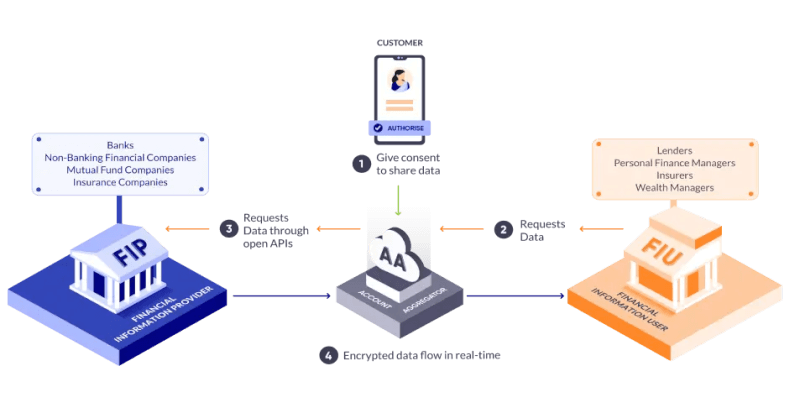
- It began with the Account Aggregator framework — making consent Open, Revocable, Granular, Auditable, Notifying and Secure (ORGANS principle).
- For model training and analytics, Privacy-Enhancing Technologies (PETs) — such as Differential Privacy — introduce mechanisms like the privacy budget to safeguard individuals while enabling learning.
- To make collaboration faster and more reliable, Electronic Contracts replace traditional paper/PDF agreements with machine-readable, enforceable commitments — cutting through the friction of slow legal processes.
- Confidential Clean Rooms (CCRs) operationalize these safeguards — enabling computation on sensitive data.
- Finally, Data Collaboratives weave all these elements together — creating institutional and economic frameworks that make responsible, long-term data collaboration practical and sustainable.
This is the next frontier of Digital Public Infrastructure for AI — proving that protection and innovation are not opposites. With the right frameworks, we can have both.
Read Part 1: Privacy in the Age of AI: New Frameworks for Data Collaboration-Part-1
Please note: The blog post is authored by our volunteers, Hari Subramanian and Sarang Galada
For more information, please visit: https://depa.world/