The internet connected the average Indian to millions of sources of information. Could crypto protocols connect Indians to millions of sources of capital?
To achieve its goal of a five trillion dollar economy by 2025, India needs to close an enormous financing gap for its small and medium-size enterprises (SMEs). It already has important assets with which to attract global capital: the youth of its population, the energy of its tech sector, the growth of its internet connectivity, and the rising acceptance of so-called informational collateral in lieu of traditional physical collateral. But what hasn’t yet been done is to integrate these assets into the new multi-trillion dollar cryptoeconomy, which may have the most risk-tolerant, internationally oriented, growth-seeking pool of investors in the world.
In this piece we begin by reviewing India’s need for SME and startup capital. We then tick through India’s existing assets, with particular focus on informational collateral, which combines the previously separate concepts of due diligence and physical collateral into an internet-friendly financing package. Finally, we discuss why global crypto investors could help meet India’s capital needs.
India’s need for SME and startup financing
India is home to more than 60 million businesses, 10 million of which have unique GST registration numbers, most of them SMEs. However, of the one trillion USD worth of total commercial lending exposure of the banking system, only ~25% of it is provided to SMEs, which are considered less creditworthy than larger corporates or multinationals. This has resulted in a financing gap estimated to be between 250-500 billion USD, where meritorious businesses without national profiles aren’t able to access the capital they need to finance their growth. India’s next trillion in GDP growth depends upon solving this problem, but the incumbent financial system may not have the resources to fix it alone. Despite ever-increasing bank branches, India’s legacy financial system is still slow, costly, and unwieldy for borrowers— in sharp contrast to the databases, online KYC systems and intelligent lending apps of new-age fintech companies. And in addition to this high cost of capital for MSMEs, India also has a low baseline level of financial inclusion.
The baseline issue is being partially addressed with low-frill Jan Dhan accounts, which are providing partial banking support for millions of previously excluded individuals. Many of these Jan Dhan accounts are held by small businesses, entrepreneurs, students and self-employed people in rural India, the same folks who are running India’s SMEs. But these accounts have only inflow data, with outflows typically in cash. Even though cash still plays a big role in the self-organized and informal sectors, it’s not easy to provide business-related financing in cash. The so-called JAM trinity (Jan Dhan accounts, Aadhaar digital identities, and Mobile phones) offers a partial solution for this under-banked population, but it only supports what we might think of as consumer-grade applications like basic peer-to-peer payments and individual savings accounts. Access to capital sufficient to finance a business — a true measure of financial inclusion — is still not yet present for these low-income, mostly feature-phone possessing groups.
On the other end of the spectrum from rural SMEs are India’s tech startups. Over the last decade, India has broken into the ranks of global technology and is now the #3 generator of unicorns in the world. Supportive governmental policies, combined with a young, creative, and aspirational workforce has helped reimagine large swathes of the economy including diverse industries such as e-commerce, logistics, SAAS, education, food, healthcare etc. This rise has attracted global equity and loan-funds that could in turn help many start-ups become world beating players in their respective domains. But the startup sector is just as hungry for capital as the rural SMEs, and India’s startup economy is still somewhat disconnected from global venture capitalists and financial markets.
India’s assets: youth, growth, connectivity, and informational collateral
India does have assets with which to close the capital gap. It has a youthful population. It has a fast-growing economy, even given the setbacks of COVID-19. It has an enormous population of hundreds of millions of new internet users. And it has something new, which is the possibility of informational collateral as a sort of combination of traditional concepts of due diligence and physical collateral.
Specifically, the SME funding gap is most pressing for the Indian cash-flow businesses that don’t have the physical assets to take out loans, which are the mainstay of the current, hard-collateral-backed credit system.
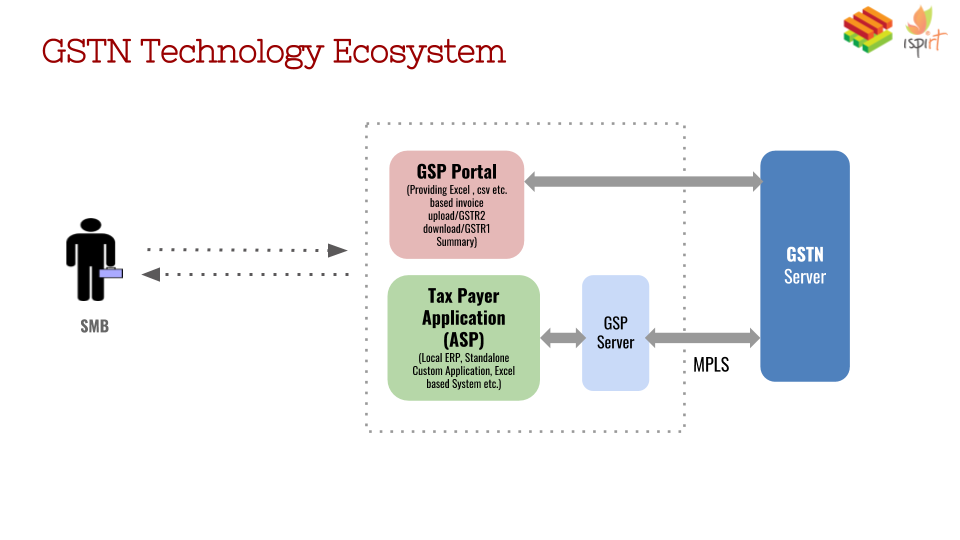
One alternative is to use trustworthy digital records to ascertain whether a business is worthy of credit or equity investment. India’s Goods and Services Tax (GST) helps to address this by generating invoice and payment data in a format suitable for credit underwriting and risk analysis. The GST data also enables a small enterprise in a large value system to provide data and visibility across the supply chain; for example, one can track the progress of parts from a small parts supplier to an auto component manufacturer to a large passenger car maker all the way through to distributors, sub-dealers, and retail sales.
The digital version of an SME’s sales and purchase invoices ledger thus amounts to informational collateral on both the company and the larger ecosystem within which it sits, that could become the basis for extending credit, as an alternative to the hard asset or collateral-based financial system. This is similar to how Square Capital and Stripe Capital already function in the West.
In addition to credit-based financing, the trustworthy records furnished by GST’s informational collateral can also support equity or quasi-equity financing, to support growth without increasing debt. These might take the form of direct equity investments in small businesses, or even personal micro-equity investments in individual consultants or students.
India’s innovation: use new pools of crypto capital to address long-standing financing needs
So, we understand that (a) Indian SMEs need capital, and that (b) IndiaStack’s UPI and Aadhaar can help GST generate informational collateral for potential investors and lenders.
Now the question arises: what class of investors is most willing to use this newfangled type of informational collateral to invest in potentially high-risk businesses outside of the proven venues of America, Europe, East Asia and the large Indian enterprises? Who are the most risk-tolerant, international, forward-looking, class of investors in the world — willing to risk millions of dollars purely on the basis of internet diligence alone?
It may turn out to be the new class of wealthy, globally-minded crypto investors. After all, the 10-year old cryptoeconomy is now worth trillions of dollars, there are more than a hundred million crypto holders around the world, and there are at least fifty crypto protocols valued over one billion dollars, a “unicoin” analog to the traditional tech unicorn. While still small in comparison to global capital markets, a sector worth $2T that is growing at more than 100% per annum could become a much larger piece of the global financial puzzle in short order. This is a new source of risk-tolerant digital capital that could flow into India to help close the SME financing gap, if we can make it an attractive proposition for the global investor.
Specifically, India could offer a viable path to deploy this new crypto wealth in a controlled manner, while solving for SME financial inclusion. Inflows of cryptocurrencies from KYC-ed investors through approved Indian and global exchanges can potentially be allowed into India for the purposes of enhancing SME access to low-cost global capital. GST-registered companies could, for instance, receive capital against their issued e-invoices and other information collateral in special accounts opened via a controlled conduit such as GIFT city, which is one of India’s favored bridges to international markets. The companies benefiting will need to explicitly consent to sharing their information and receiving funds into a new account at system-level while capturing cash flows against invoices for repayment. Inflows of global crypto-capital into Indian SMEs could also enable the rest of the credit system to migrate to informational collateral-based lending. And the special account could eventually be ported to a wallet backed by a national digital currency, such as the proposed digital rupee.
For more detail on this possibility, we invite your attention to Balaji S. Srinivasan’s companion piece on the subject, where he proposes to Add Crypto To IndiaStack. Balaji makes the case for crypto-powered extension of IndiaStack, which broadens IndiaStack from its current mostly domestic remit into an international platform for attracting capital from around the world. He describes several case studies by which the emerging world of decentralized finance or “defi” could help enrich the Indian economy, without competing with the digital rupee. For example, Indian startups could benefit from crypto crowdfunding, Indian SMEs as discussed could access global defi lending pools, and Indian students might even be funded with the emerging concept of personal tokens, like an equity-based version of microfinance. As the former CTO of Coinbase, the $100B crypto goliath, and a former General Partner at Andreessen Horowitz, the $16B venture capital firm, Balaji’s proposals have technical and social support from the very class of investors we’d seek to attract. At least insofar as they relate to the issue of plugging the SME financing gap, we believe they deserve serious consideration by policymakers in India.
In short, India has a unique opportunity to close the SME financing gap by attracting the new class of global crypto investors, by using everything the IndiaStack team has helped build over the last decade — particularly UPI, Aadhaar, GST, and the informational collateral they generate — to help connect the trillion-dollar cryptoeconomy to capital-hungry Indian entrepreneurs.
The blog post is co-authored by Sanjay Phadke, Krishna V Iyer, Pankaj Gupta, Sanjay Jain, Sharad Sharma and Siddharth Shetty.
For any further queries, please write to sanjay.phadke@ispirt.in











 In fact, if you actually ponder, you would perceive that the real driver of this phenomenon has been something else entirely. It is the proliferation of ‘shared economy’ lifestyle that makes these social use cases so prominent and common for us.
In fact, if you actually ponder, you would perceive that the real driver of this phenomenon has been something else entirely. It is the proliferation of ‘shared economy’ lifestyle that makes these social use cases so prominent and common for us. This brings us full circle to the two golden philosophies that have stood the test of time again and again –
This brings us full circle to the two golden philosophies that have stood the test of time again and again –