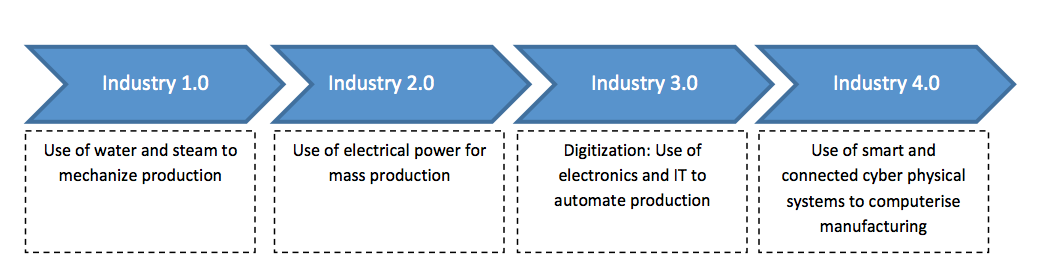
In case you are a manufacturing company beginning to explore how investment into Artificial Intelligence and Internet of Things could help your top and bottom lines, you may already have fallen behind. The fourth industrial revolution or the ‘Industry 4.0’ is already upon us and the opportunities to completely transform the way we carry out production are limitless. Industry 4.0 may be broadly defined as a collective term for a number of contemporary automation, data exchange and manufacturing technologies. It is characterised by a diminishing boundary between the cyber and physical systems to enhance productivity and reduce costs. ‘Smart’ and ‘Connected’ are two of the most important keywords in the new industry universe. Smart takes us into the domain of Artificial Intelligence (AI) while ‘Connected’ is more a purview of ‘Internet of Things’ (IoT).
‘Smart’ – A detour into Artificial Intelligence
AI finds its roots way back in 1956 when the name ‘Artificial Intelligence’ was adopted or even further back with Alan Turing in 1950 or in 1943 when McCulloch & Pitts introduced the Boolean circuit model of brain. It’s still however, a little difficult to settle on one universal definition of AI. For our purpose we may define AI as the development of computer systems able to perform tasks normally requiring human intelligence. These may include (but are not limited to) visual perception, speech recognition, decision-making, and translation between languages. More passionate people define AI as the ability to ‘solve new problems’.
The lack of one single definition has not detracted investors from recognizing the potential of AI and they have been pouring in money like never before. As per Zinnov Consulting, in the last 5 years alone, investments in AI have grown ten-fold from USD 94 million in 2011 to USD 1billion in 2016. As per CB Insights, the equity investments in AI were North of USD 2 billion in both 2014 and 2015. We may attribute different ways of defining AI to different investment figures, however we can agree that investments have sky rocketed. While, Venture capital firms have obviously been at the forefront in backing early stage companies, the high corporate interest in acquiring AI start-ups has also led to a buzz in the M&A markets. Some of the biggest acquirers in AI include Google, Apple, Salesforce, Amazon, Microsoft, Intel and IBM.
India is holding its own in terms of AI related action. As per Zinnov, India has emerged as the 3rd largest AI ecosystem in the world with 170 start-ups. Niki.ai, SnapShopr, YANA, HealthNextGen, Aindra Systems, Hire Alchemy are some of the notable firms trying to disrupt the value chain across sectors. Global technology companies have acquired more than half-a-dozen India based AI start-ups in the last 18 months. It’s not all one way traffic. Indian IT services firms like Infosys (UNSILO, Cloudyn, TidalScale) and Wipro (Vicarious, Vectra Ventures) have been looking for targets abroad to augment their AI capabilities.
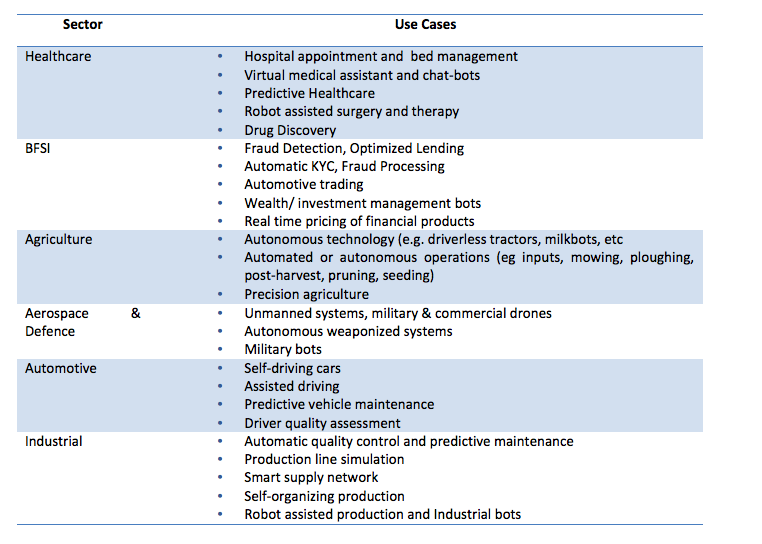
Table 1: AI use cases across sectors
‘Connected’ – the Industrial IoT
The Industrial Internet of Things refers to the network of equipment which includes a very large volume of sensors, devices and “things” that produce information and add value to the manufacturing processes. This information or data acts a feed to the AI systems. As per Cisco, 50 billion devices will be connected by 2020 and 500 billion by 2030. McKinsey projects that IoT will generate 11% of global GDP by 2025. This is driven by optimising industry performance and cost efficiencies.
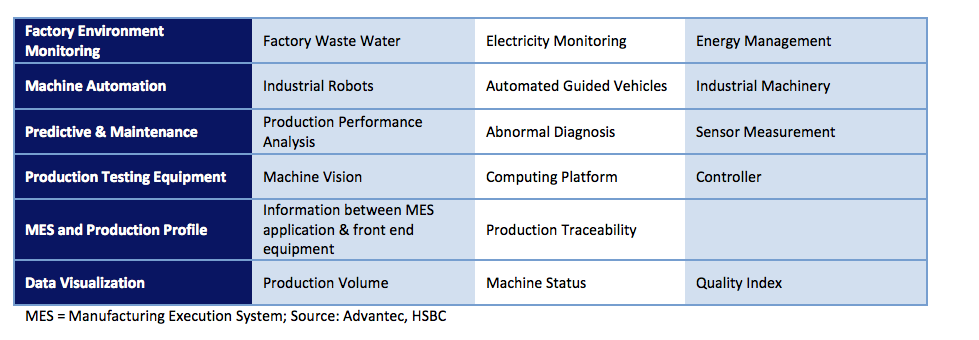
IIoT on the Factory Floor
The global IIoT spending is estimated at USD 250 billion and is expected to reach USD 575 billion by 2020. The key components of the IIoT ecosystem include sensors/modules, connectivity, customisation, and platform/IoT cloud/applications.
As per NASSCOM, The Indian IoT market is expected to reach USD 15 billion with 2.7 billion units by 2020 from the current USD 5.6 billion and 200 million connected units. This is expected to be largely driven by applications in manufacturing, automotive and transportation and logistics.
In India, the IIoT segment has caught the attention of the largest manufacturers. In November 2016, Reliance and GE announced a partnership to work together to build applications for GE’s Predix platform. The partnership will provide industrial IoT solutions to customers in industries such as oil and gas, fertilizers, power, healthcare and telecom. Mahindra & Mahindra’s uses bots to build car body frames at its Nashik plant. Plants operated by Godrej and Welspun use the Intelligent Plant Framework provided by Covacis Technologies to run their factory floors.
Industry 4.0 is an exciting phase and the possibilities seem limitless. The Indian government is trying to play its part through the Digital India mission. It is positively driving various government projects such as smart cities, smart transportation, smart grids, etc. which are also expected to further propel the use of IoT technology. It is imperative for the promoters and companies in the manufacturing segment to find their place in the new digital world order through organic or inorganic investment.
This is a guest post by Arvind Yadav,
Principal at Aurum Equity Partners LLP.