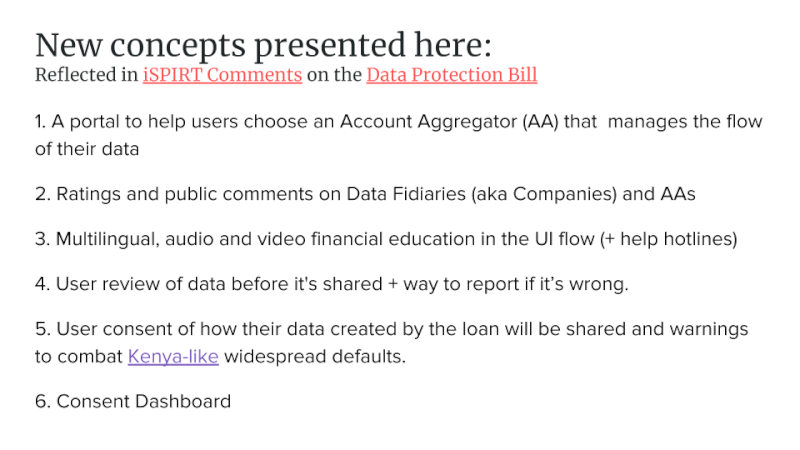
Below represents iSPIRT’s comments and recommendations on the draft Personal Data Protection Bill. iSPIRT’s overall data privacy and data empowerment philosophy is covered here.
Table of Contents
Major Comments
1. Include Consent Dashboards
2. Financial Understanding and Informed Consent for all Indians
3. Data Fiduciary Trust Scores Similar to App Store Ratings
4. Comments & Complaints on Data Fiduciaries are Public, Aggregatable Data
5. Warn of Potential Credit and Reputation Hazards
6. A Right to View and Edit Inferred Personal Data
7. Sharing and Processing of Health Data
Suggestions and Questions
- Fund Data Rights Education
- Limit Impact Assessment Requirement
- Passwords should be treated differently than other Sensitive Personal Data.
- Does the Bill intend to ban automatic person-tagging in photos and image search of people?
- Notifications about updates to personal data should be handled by a Consent Dashboard, not every data fiduciary.
- Need for an Authority appeal process when data principal rights conflict
- Do not outlaw private fraud detection
- Limit record keeping use and disclosure to the Authority and the company itself.
- Fillings may be performed digitally
- Request for Definition Clarifications
- Author Comments
- Links
- Appendix – Sample User Interface Screens
Major Comments
1. Include Consent Dashboards
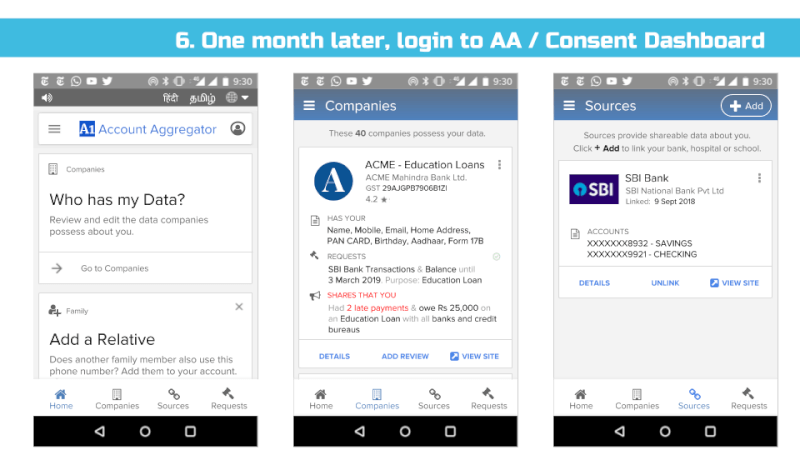
We support the idea of a Consent Dashboard as suggested in the Data Protection Committee Report (page 38) and recommend it to be incorporated in the Bill in Section 26 – Right to Data Portability and Section 30 (2) Transparency.
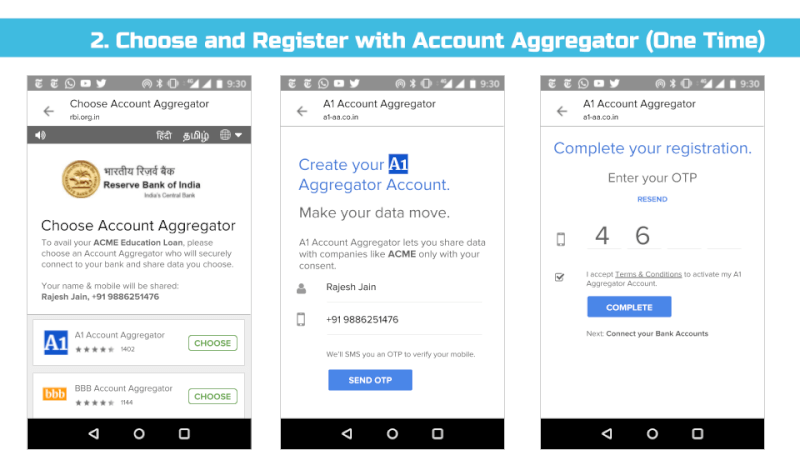
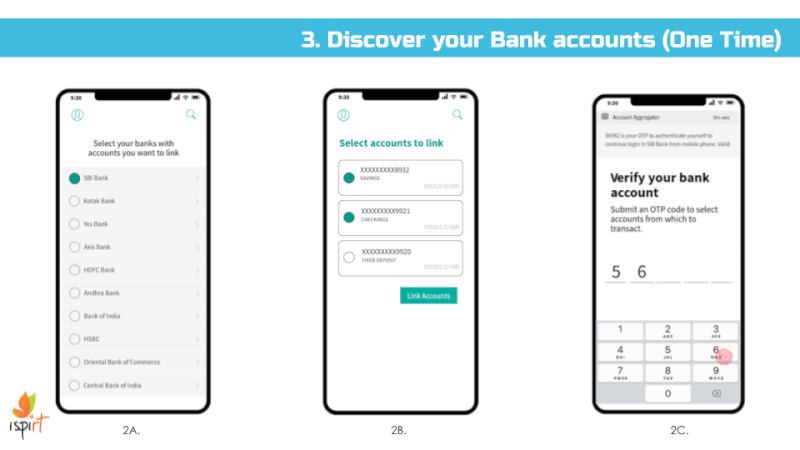
We envision all of a user’s personal and inferred data that is known by data fiduciaries (i.e. companies) being exposed on a consent dashboard, provided by a third party consent collector or account aggregator (to use the RBI’s parlance). Below is an example user interface:
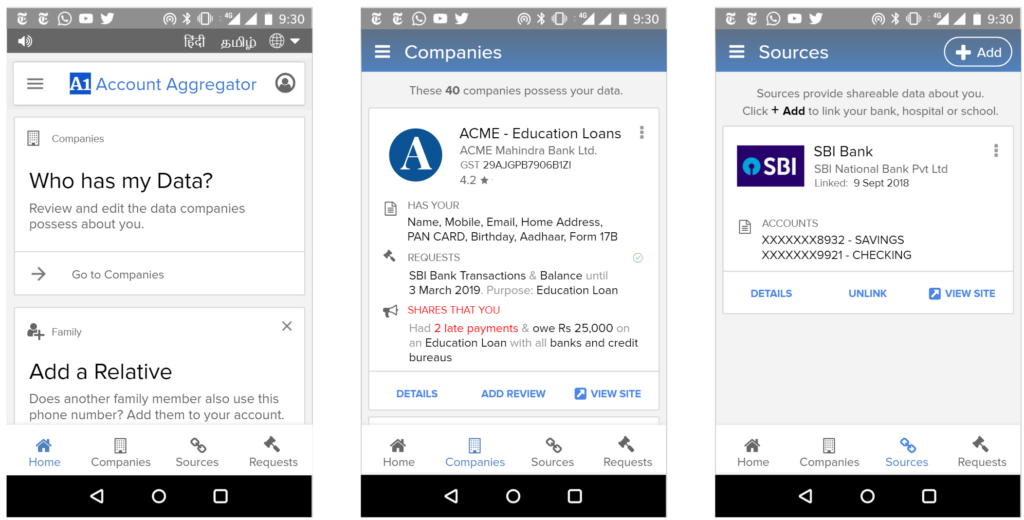
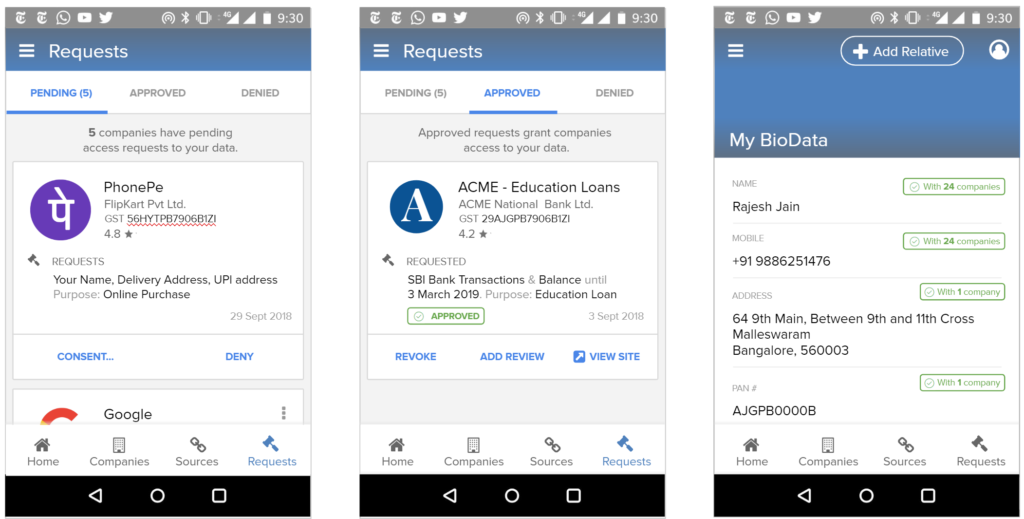
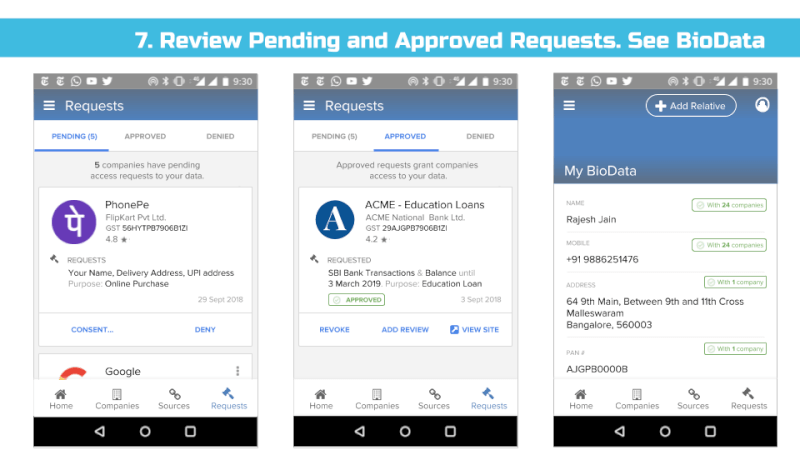
This mandate would enable users to have one place – their consent collector-provided dashboard – to discover, view and edit all data about them. It would also allow users to see any pending, approved and denied data requests.
Furthermore, in the event of data breaches, especially when a user’s password and identifier (mobile, email, etc) have been compromised, the breach and recommended action steps could be made clear on the consent dashboard.
Given the scope of this suggestion, we recommend an iterative or domain specific approach, wherein financial data is first listed in a dashboard limited to financial data and for its scope to grow with time.
2. Financial Understanding and Informed Consent for all Indians
We applaud the Bill’s Right to Confirmation and Access (Chapter IV, Section 24):
The data fiduciary shall provide the information as required under this section to the data principal in a clear and concise manner that is easily comprehensible to a reasonable person.
That said, we’ve found in practice that it’s difficult to appreciate the implications of digital policies on users until real user interfaces are presented to end users and then tested for their usability and understanding. Hence, we’ve put together a set of sample interfaces (see Appendix) that incorporate many of the proposed bill’s provisions and our recommendations. That said, much more work is needed before we can confidently assert that most Indians understand these interfaces and what they are truly consenting to share.
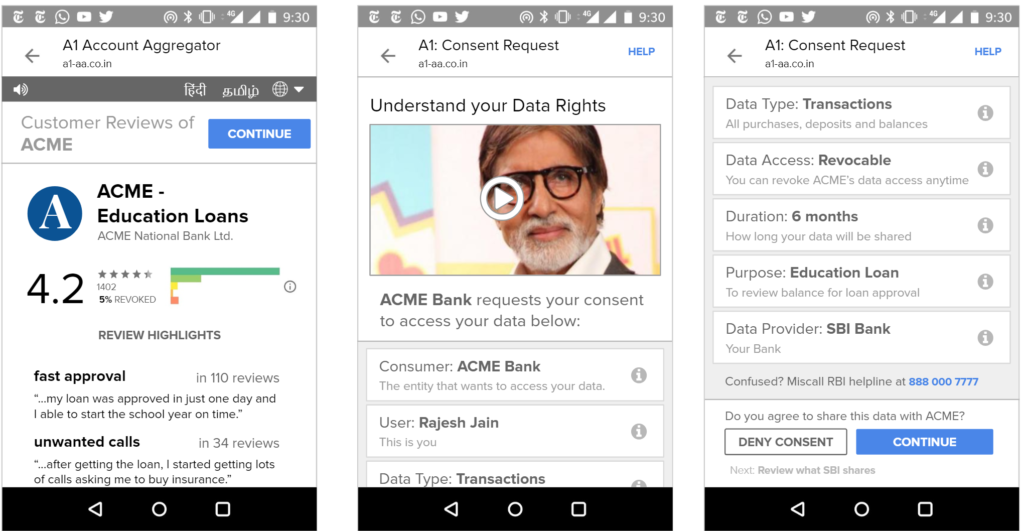
The concepts behind this bill are complicated and yet important. Most people do not understand concepts such as “revocable data access rights” and other rather jargon-filled phrases often present in the discussion of data privacy rights. Hence, we believe the best practices from interface design must be employed to help all Indians – even those who are illiterate and may only speak one of our many non-dominant languages – understand how to control their data.
For example, multi-language interfaces with audio assistance and help videos could be created to aid understanding and create informed consent. Toll-free voice hotlines could be available for users to ask questions. Importantly, we recognize that the interfaces of informed consent and privacy control need rigorous study and will need to evolve in the years ahead.
In particular, we recommend user interface research in the following areas:
- Interfaces for low-education and traditionally marginalized communities
- Voice-only and augmented interfaces
- Smart and “candy-bar” phone interfaces
- Both self-serving and assisted interfaces (such that a user can consensually and legally delegate consent, as tax-payers do to accountants).
After user interface research has been completed and one can confidently assert that certain interface patterns can be understood by most Indian adults, we can imagine that templated designs representing best practices are recommended for the industry, much like the design guidelines for credit card products published by US Consumer Financial Protection Bureau or nutritional labelling.
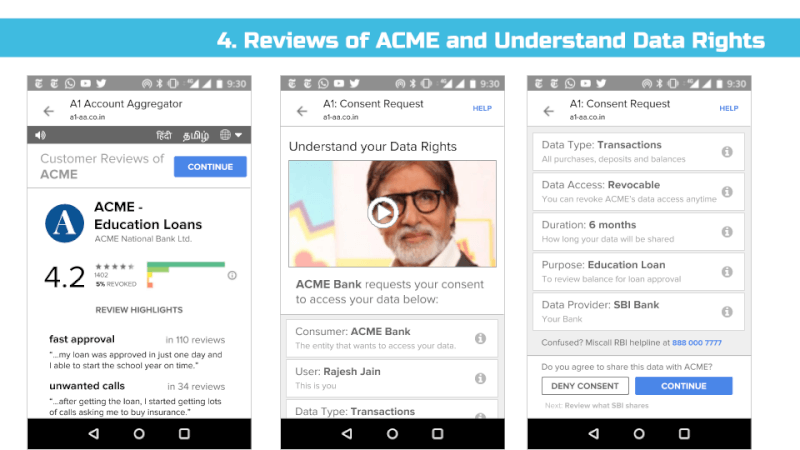
3. Data Fiduciary Trust Scores Similar to App Store Ratings
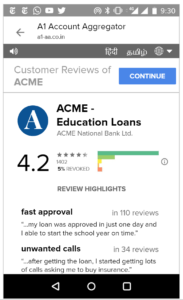
We support the government’s effort to improve the trust environment and believe users should have appropriate, easy and fast ways to give informed consent & ensure bad actors can’t do well. Conversely, we believe that the best actors should benefit from a seamless UI and rise to the top.
The courts and data auditors can’t be the only way to highlight good, mediocre and bad players. From experience, we know that there will be a continuum of good to bad experiences provided by data fiduciaries, with only the worst and often most egregious actions being illegal.
People should be able to see the experiences of other users – both good and bad – to make more meaningful and informed choices. For example, a lender that also cross-sells other products to loan recipients and shares their mobile numbers may not be engaging in an illegal activity but users may find it simply annoying.
Hence, we recommend that data fiduciary trust scores are informed with user-created negatives reviews (aka complaints) and positive reviews.
In addition to Data Auditors (as the Bill envisions), user created, public ratings will create additional data points and business incentives for data fiduciaries to remain in full compliance with this law, without a company’s data protection assessment being the sole domain of its paid data auditors.
We would note that crowd sourced rating systems are an ever-evolving tech problem in their own right (and subject to gaming, spam, etc) and hence, trust rating and score maintenance may be best provided by multiple market actors and tech platforms.
4. Comments & Complaints on Data Fiduciaries are Public, Aggregatable Data
…so 3rd party actors and civil society can act on behalf of users.
A privacy framework will not change the power dynamics of our society overnight. Desperate people in need of money will often sign over almost anything, especially abstract rights. Additionally, individual citizens will rarely to be able to see larger patterns in the behaviour of lenders or other data fiduciaries and are ill-equipped to fight for small rewards on behalf of their community. Hence, we believe that user ratings and complaint data about data fiduciaries must be made available in machine-readable forms to not only to the State but to third-parties, civic society and researchers so that they may identify patterns of good and bad behaviour, acting as additional data rights watchdogs on behalf all of us.
5. Warn of Potential Credit and Reputation Hazards
We are concerned about the rise of digital and mobile loans in other countries in recent years. Kenya – a country with high mobile payment penetration and hence like India one that has become data rich before becoming economically rich – has seen more than 10% of the adult population on credit blacklists in 2017; three percent of all digital loans were reportedly used for gambling. These new loan products were largely made possible by digital money systems and the ability of lenders to create automated risk profiles based on personal data; they clearly have the potential to cause societal harm and must be considered carefully.
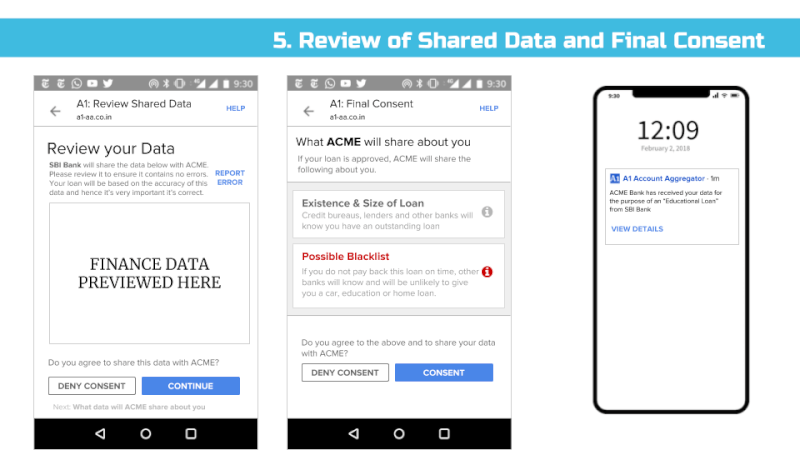
Potential remedies to widespread and multiple loans are being proposed (e.g. real-time credit reporting services), but the fact that a user’s reputation and credit score will be affected by an action (such as taking out a loan), most also be known and understood by users. E.g. Users need to know that an offered loan will be reported to other banks and if they don’t pay they will be reported and unable to get other loans.
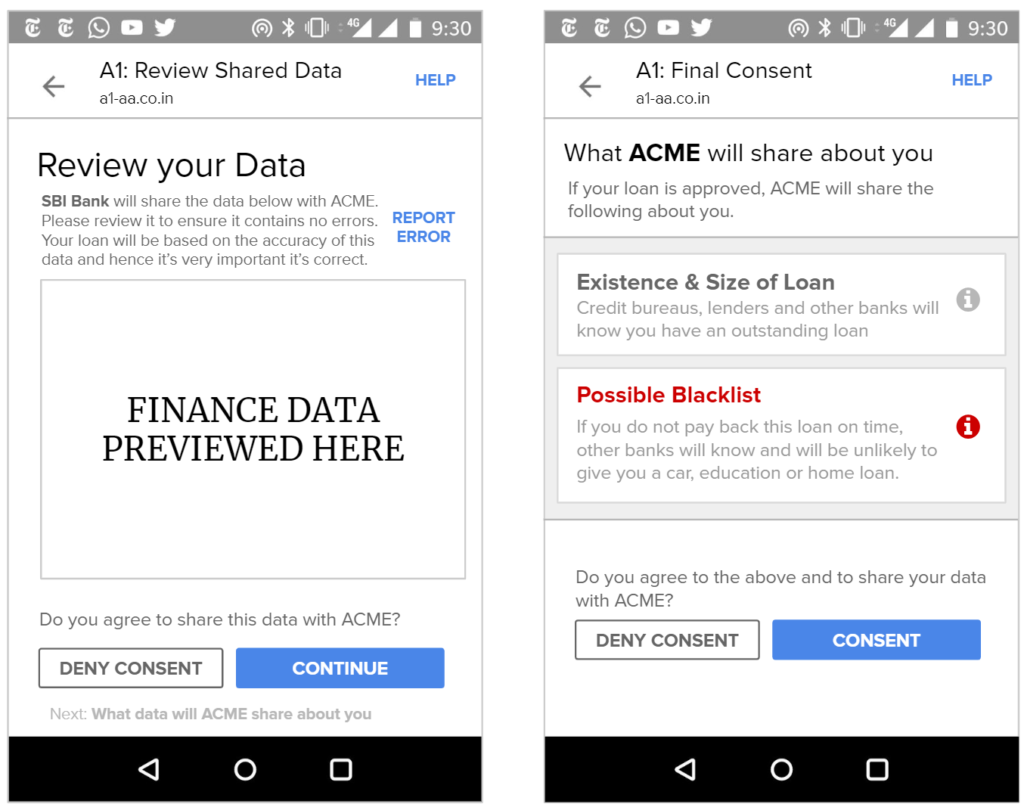
Furthermore, shared usage-based patterns – such as whether a customer pays their bills on time or buys certain types of products – must be available for review by end users.
6. A Right to View and Edit Inferred Personal Data
The Machine Learning and AI community have made incredible strides in computers’ ability to predict or infer almost anything. For example, in 2017, a babajob.com researcher showed the company could predict whether a job seeker earned more or less than Rs 12000 / month with more than 80% accuracy, using just their photo. She did this using 3000 job seeker photos, 10 lines of code and Google’s TensorFlow for Poets sample code. Note the project was never deployed or made publicly available.
As these techniques become ever more commonplace in the years to come, it’s reasonable to assume that public facing camera and sensor systems will be able to accurately infer most of the personal data of their subjects – e.g. their gender, emotional state, health, caste, religion, income – and then connect this data to other personally identifiable data such as a photo of their credit card and purchase history. Doing so will improve training data so that systems become even more accurate. In time, these systems – especially ones with large databases of labelled photos – like the governments’, popular social networks’ or a mall’s point of sale + video surveillance system – truly will be able to precisely identify individuals and their most marketable traits from any video feed.
Europe’s GDPR has enshrined the right for people to view data inferred about them, but in conjunction with the idea of a third party consent dashboard or Account Aggregator (in the RBI’s case), we believe we can do better.
In particular, any entity that collects or infers data about an individual that’s associated with an identifier such as an email address, mobile, credit card, or Aadhaar number should make that data viewable and editable to end users via their consent dashboard. For example, if a payment gateway provider analyses your purchase history and infers you are diabetic and sells this information as a categorization parameter to medical advertisers, that payment gateway must notify you that it believes you are diabetic and enable you to view and remove this data. Google, for example, lists these inferences as Interests and allows users to edit them:
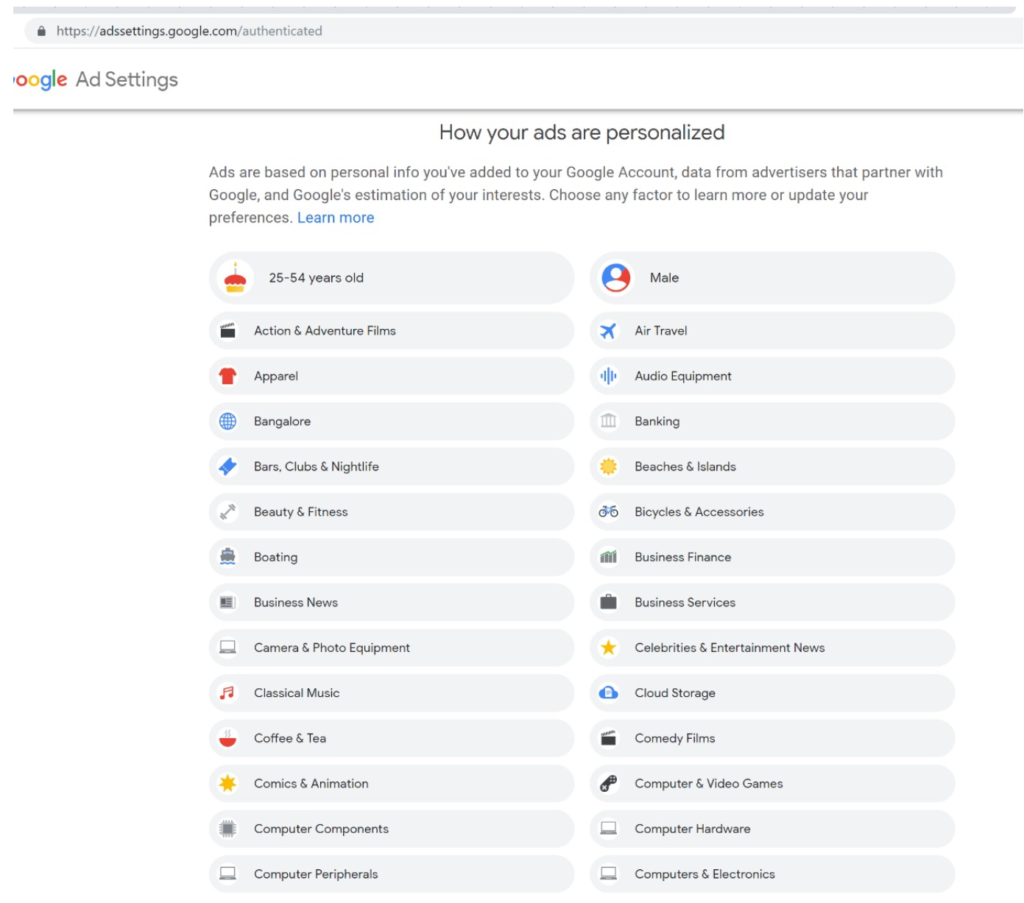
Using the Consent Dashboard mentioned in Major Comment 1, we believe users should have one place where they can discover, view and correct all personal and inferred data relevant to them.
Finally, more clarity is needed regarding how data gathered or inferred from secondary sources should be regulated and what consent may be required. For example, many mobile apps ask for a user’s consent to read their SMS Inbox and then read their bank confirmation SMSs to create a credit score. From our view, the inferred credit score should be viewable by the end user before it’s shared, given its personal data that deeply affects the user’s ability to gain usage of a service (in this case, often a loan at a given interest rate).
7. Sharing and Processing of Health Data
The Bill requires capturing the purpose for data sharing:
Chapter II, point 5:
“Purpose limitation.— (1) Personal data shall be processed only for purposes that are clear, specific and lawful. (2) Personal data shall be processed only for purposes specified or for any other incidental purpose that the data principal would reasonably expect the personal data to be used for, having regard to the specified purposes, and the context and circumstances in which the personal data was collected.”
In the healthcare domain, collecting the purpose for which the data is being shared might itself be quite revealing. For example, if data is being shared for a potential cancer biopsy or HIV testing, the purpose might be enough to make inferences and private determinations about the patient and say deny insurance coverage. On the other hand, stating high-level, blanket purposes might not be enough for future audits. A regulation must be in place to ensure the confidentiality of the stated purpose.
The Bill has a provision for processing sensitive personal data for prompt action:
Chapter IV, point 21:
“Processing of certain categories of sensitive personal data for prompt action. — Passwords, financial data, health data, official identifiers, genetic data, and biometric data may be processed where such processing is strictly necessary— (a) to respond to any medical emergency involving a threat to the life or a severe threat to the health of the data principal; (b) to undertake any measure to provide medical treatment or health services to any individual during an epidemic, outbreak of disease or any other threat to public health; or (c) to undertake any measure to ensure safety of, or provide assistance or services to, any individual during any disaster or any breakdown of public order.”
While this is indeed a necessity, we believe that a middle ground could be achieved by providing an option for users to appoint consent nominees, in a similar manner to granting power of attorney. In cases of emergency, consent nominees such as family members could grant consent on behalf of the user. Processing without consent could happen only in cases where a consent nominee is unavailable or has not been appointed. This creates an additional layer of protection against misuse of health data of the user.
Suggestions and Questions
Fund Data Rights Education
We believe a larger, public education program may be necessary to educate the public on their data rights.
Limit Impact Assessment Requirement
Section 33 – Data Protection Impact Assessment —
- Where the data fiduciary intends to undertake any processing involving new technologies or large scale profiling or use of sensitive personal data such as genetic data or biometric data, or any other processing which carries a risk of significant harm to data principals, such processing shall not be commenced unless the data fiduciary has undertaken a data protection impact assessment in accordance with the provisions of this section. …
- On receipt of the assessment, if the Authority has reason to believe that the processing is likely to cause harm to the data principals, the Authority may direct the data fiduciary to cease such processing or direct that such processing shall be subject to such conditions as may be issued by the Authority.
We believe that the public must be protected from egregious data profiling but this provision does not strike an appropriate balance with respect to innovation. It mandates that companies and other researchers must ask government permission to innovate around large scale data processing before any work, public deployments or evidence of harm takes place. We believe this provision will be a large hinderance to experimentation and cause significant AI research to simply leave India. A more appropriate balance might be to ask data fiduciaries to privately create such an impact assessment but only submit to the Authority for approval once small scale testing has been completed (with potential harms better understood) and large scale deployments are imminent.
Passwords should be treated differently than other sensitive personal data.
Chapter IV – Section 18. Sensitive Personal Data. Passwords are different than other types of Sensitive Personal Data, given that they are a data security artifact, rather than a piece of data that is pertinent to a person’s being. We believe that data protection should be over-ridden in extraordinary circumstances without forcing companies to provide a backdoor to reveal passwords. We fully acknowledge that it is useful and sometimes necessary to provide backdoors to personal data – e.g. one’s medical history in the event of a medical emergency – but to require such a backdoor for passwords would likely introduce large potential security breaches throughout the entire personal data ecosystem.
Does the Bill intend to ban automatic person-tagging in photos and image search of people?
Chapter I.3.8 – Biometric Data – The Bill defines Biometric Data to be:
“facial images, fingerprints, iris scans, or any other similar personal data resulting from measurements or technical processing operations carried out on physical, physiological, or behavioural characteristics of a data principal, which allow or confirm the unique identification of that natural person;”
The Bill includes Biometric Data in its definition of Sensitive Personal Data (section 3.35) which may only be processed with explicit consent:
Section 18. Processing of sensitive personal data based on explicit consent. — (1) Sensitive personal data may be processed on the basis of explicit consent
From our reading, we can see a variety of features available today around image search and person tagging being disallowed based on these provisions. E.g. Google’s image search contains many facial images which have been processed to enable identification of natural persons. Facebook’s “friend auto-suggestion” feature on photos employs similar techniques. Does the Bill intend for these features and others like them to be banned in India? It can certainly be argued that non-public people have a right to explicitly consent before they are publicly identified in a photo but we feel the Bill’s authors should clarify this position. Furthermore, does the purpose of unique identification processing matter with respect to its legality? For example, we can imagine mobile phone-based, machine learning algorithms automatically identifying a user’s friends to make a photo easier to share with those friends; would such an algorithm require explicit consent from those friends before it may suggest them to the user?
Notifications about updates to personal data should be handled by a Consent Dashboard, not every data fiduciary.
Chapter IV – Section 25.4 – Right to correction, etc
Where the data fiduciary corrects, completes, or updates personal data in accordance with sub-section (1), the data fiduciary shall also take reasonable steps to notify all relevant entities or individuals to whom such personal data may have been disclosed regarding the relevant correction, completion or updating, particularly where such action would have an impact on the rights and interests of the data principal or on decisions made regarding them.
We believe the mandate on a data fiduciary to notify all relevant entities of a personal data change is too great a burden and is better performed by a consent dashboard, who maintains which other entities have a valid, up-to-date consent request to a user’s data. Hence, upon a data change, the data fiduciary would update the consent dashboard of the change and then the consent dashboard would then notify all other relevant entities.
It may be useful to keep the user in this loop – so that this sharing is done with their knowledge and approval.
Need for an Authority appeal process when data principal rights conflict
Section 28.5 – General conditions for the exercise of rights in this Chapter. —
The data fiduciary is not obliged to comply with any request made under this Chapter where such compliance would harm the rights of any other data principal under this Act.
This portion of the law enables a data fiduciary to deny a user’s data change request if it believes doing so would harm another data principal. We believe it should not be up to the sole discretion of the data fiduciary to determine which data principal rights are more important and hence would like to see an appeal process to the Data Protection Authority made available if a request is refused for this reason.
Do not outlaw private fraud detection
Section 43.1 Prevention, detection, investigation and prosecution of contraventions of law
(1) Processing of personal data in the interests of prevention, detection, investigation and prosecution of any offence or any other contravention of law shall not be permitted unless it is authorised by a law made by Parliament and State Legislature and is necessary for, and proportionate to, such interests being achieved.
We worry the above clause would effectively outlaw fraud detection research, development and services by private companies in India. For instance, if a payment processor wishes to implement a fraud detection mechanism, they should be able to do so, without leaving that task to the State. These innovations have a long track record of protecting users and businesses and reducing transaction costs. We recommend a clarification of this section and/or its restrictions to be applied to the State.
Limit record keeping use and disclosure to the Authority and the company itself.
Section 34.1.a. Record – Keeping –
The data fiduciary shall maintain accurate and up-to-date records of the following
(a) important operations in the data life-cycle including collection, transfers, and erasure of personal data to demonstrate compliance as required under section 11;
We expect sensitive meta-data and identifiers will need to be maintained for the purposes of Record Keeping; we suggest that this Record Keeping information be allowed but its sharing limited only to this use and shared only with the company, its Record Keeping contractors (if any) and the Authority.
Fillings may be performed digitally
Section 27.4 – Right to be Forgotten
The right under sub-section (1) shall be exercised by filing an application in such form and manner as may be prescribed.
The Bill contains many references to filing an application; we’d suggest a definition that is broad and includes digital filings.
This also applies to sections which include “in writing” – which must include digital communications which can be stored (for instance, email).
Request for Definition Clarifications
What is “publicly available personal data”?
- Section 17.2.g – We believe greater clarity is needed around the term “publicly available personal data.“ There questionably obtained databases for sale that list the mobile numbers and addresses of millions of Indians – would there thus be included as a publicly available personal data?
- We’d recommend that DPA defines rules around what is publicly available personal data so that it is taken out of the ambit of the bill.
- The same can be said for data where there is no reasonable expectation of privacy (with the exception that systematic data collection on one subject cannot be considered to be such a situation)
Clarity of “Privacy by Design”
Section 29 – Privacy by Design
Privacy by Design is an established set of principles (see here and in GDPR) and we would like to see the Bill reference those patterns explicitly or use a different name if it wishes to employ another definition.
Define “prevent continuing disclosure”
Section 27.1 – Right to be Forgotten
The data principal shall have the right to restrict or prevent continuing disclosure of personal data by a data fiduciary…
We request further clarification on the meaning of “prevent continuing disclosure” and an example use case of harm.
Define “standard contractual clauses” for Cross-Border Transfers
Section 41.3.5 – Conditions for Cross-Border Transfer of Personal Data
(5) The Authority may only approve standard contractual clauses or intra-group schemes under clause (a) of sub-section (1) where such clauses or schemes effectively protect the rights of data principals under this Act, including in relation with further transfers from the transferees of personal data under this subsection to any other person or entity.
We would like to standard contractual clauses clearly defined.
Define “trade secret”
Section 26.2 C – Right to be Forgotten
compliance with the request in sub-section (1) would reveal a trade secret of any data fiduciary or would not be technically feasible.
We request further clarification on the meaning of “trade secret” and an example of the same.
Author Comments
Compiled by iSPIRT Volunteers:
- Sean Blagsvedt – sean _@_ blagsvedt.com
- Siddharth Shetty – siddharth _@_ siddharthshetty.com
- Anukriti Chaudhari – anukriti.chaudhari _@_ gmail.com
- Sanjay Jain – snjyjn _@_ gmail.com
Links
Comments and feedback are appreciated. Please mail us at [email protected].
Appendix – Sample User Interface Screens
Link: https://docs.google.com/presentation/d/1Eyszb3Xyy5deaaKf-jjnu0ahbNDxl7HOicImNVjSpFY/edit?usp=sharing
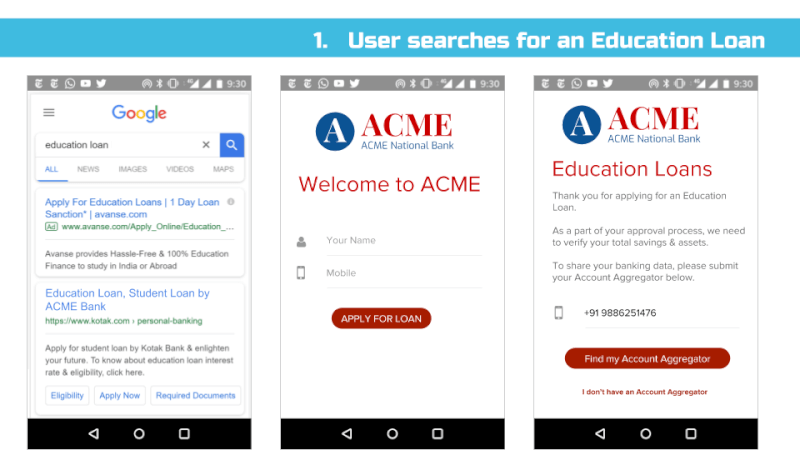
******


















