In innumerable brainstorming and “gyan” sessions with friends, mentors and experts, one of the most stressed focus area is getting product market fit as soon as possible and then follow it up with scaling sales. I think most early to mid stage entrepreneurs are instinctively aware of this but struggling with “Hows”. So when I saw this playbook promising precisely to explain how, I grabbed a spot. I wasn’t disappointed. Suresh Sambandam is very down to earth and spoke earnestly and in detail about different steps he took while selling the OrangeScape’s product KiSSFLOW. Attendees who themselves run early to mid-stage companies and Kishore Mandyam of Impel CRM chipped in with their stories and inputs. Here is the detailed enough capture of the same.
The relevancy of this session is greatest to Early and Mid-stage entrepreneurs going from $0-5K MRR to $50K MRR selling to US MSB. This session is NOT meant for discovery or product market fit but I have inserted the discussion at the end.
The blog is organised as below Product Market Fit / Pricing as step 0; Followed by Inbound Sales and Marketing and then finally Outbound Sales and discussion on tools.
 Product Market Fit
Product Market Fit
The absolute first step (may be zeroth step) in Sales process is getting the product market fit. You know you have a Product Market Fit with a B2B Mid-Market SaaS product when unknown folks start buying (Inbound sales is picking up traction). Unfortunately in cases that were presented at the session, the discovery process of the product happened organically based on another product that they were building.
However the generic solution for early stage product discovery goes like this.
-
Create a landing page with a “notify when ready”.
-
Create a SEO/Adword campaign for getting early adopters. You need to be very clear about the product category and fine tune your Adwords to exactly match what product aspires to solve. There are usually two approaches to any product i.e Disruptive Innovator or Faster Better Cheaper. So Adwords need to be in line with these
-
Once people signup engage with them and partner with them to fine tune the product.
To put succinctly Bring-> Engage->Convert->Succeed; As you can clearly see from this model, “Marketing Comes Before Product” or as Suresh puts it bring the horse to the water.
Pricing and “Freemium v/s Free Trial”
So which model suits best for a SaaS product? Is there one preferable over another? Very subjective topic but the thumb rule seems to be for SMB / Mid-market SaaS Free Trial is a best method to go.
Models aside, what matters most to the conversion is the post-signup engagement and the price factor. Faster conversions are dependent on many factors but one of the key factors is pricing. If pricing is within the decision-making authority of the midlevel managers, it is easier to convert. The discretionary spending seems to be around about USD 5K. Keeping the price low per user and making minimum unit purchase of say 10 users per bundle works quite great.
Inbound Sales
WebSite – Suresh firmly believes that Website is a core asset for a B2B SaaS company and hence should not be outsourced. He advises to have a minimum team of Web Developer, Creative Designer and Automation Engineer. This would help perpetual A/B testing in short cycles..
Couple of nifty tricks to make the whole experience frictionless is to have a one click signup. Visitor should be able to experience the main software within few seconds. The other participating companies in the round table have used various techniques to authenticate emails like SMTP Ping, email pattern matching, etc.
It is also important to closely monitor the users interaction with the website, capture it and feed it back to the Engineers to close the gap and arguments between Sales/Marketing and Engineering. One of the recommended tools in this category is FullStory.
 SEO
SEO
Lot of interesting debates on this; discussion ranged from how get the right keywords for searches and what optimization works and how to track the metrics. Suresh again firmly believes in having a dedicated SEO guy and focus on defined key words. They manage about 28 keywords and track them very meticulously. Some thumb rules and objectives again are
- Do it Slowly but Steady
- Don’t alert Google
- Build Backlinks (Naked and Anchor)
- Improve Google Crawl Frequency
Adwords:
It is preferable to have one dedicated person with number crunching and finance background. This will help track the cost per signup for search ads
Content Generation:
While it is important to have this come from founders, it is very hard to find time for the founders. One technique employed by KiSSFLOW is to hire fresher from visual communication background who has a grammar nazi attitude and give a very specific target like 2 +2+2+1 per week (2 blogs published 2 interviews done, 2 assured interviews for next week and 1 research post). He also uses 10-80-10 formula for the content itself where beginning 10 and ending 10 percent are reviewed in detail by founders. One of the other key points stressed was to have self ads in each of the content which leads to signup.
Outbound Sales
Contact DB
Obviously the most critical first step here is having a database of all the companies and the decision makers that you want to reach out. Linkedin Premium works best. This is how Suresh does it. He uses Linkedin DB to create a list of all target companies and then assigns the task of creating the contact details to an online consultant who was discovered on Elance. It usually works out to INR6-INR10 per contact. There are other dbs one can purchase directly from companies such as Data.com, Discover, rainking and slew of others.
Once contacts are obtained it is very important to use direct emails as opposed to using mailchimp, constantcontact, etc as most of them will not land in inbox. It also helps to be as personalized as possible.
Sales DNA
It is absolutely essential for the founder to set the tone of sales. For US be ready to pull night shifts continuously. Although it is the founders calling, it is good idea to assume the persona that appeals to US clients say Bob and position one as a sales manager. It is also important to make the sales hire to listen to the call handling to build on this.
Channels
Not all channels are suitable for SaaS and one needs to do some trial and error to figure out the best channels. The channels include Events, Road Shows, Reselling Partners and Referral/Affiliate partners, may work well but Orangescape has ignored them.
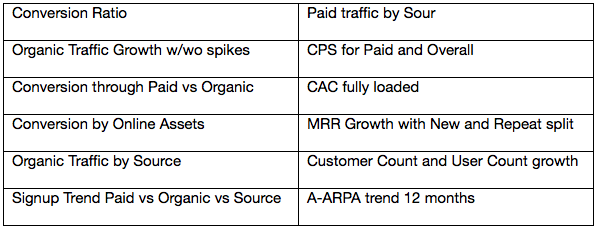
Metrics, Tracking, Tools
Meticulous tracking is critical and many tools are available to manage and measure the process. Some that are being used by the roundtable companies are listed below.
Metrics to track
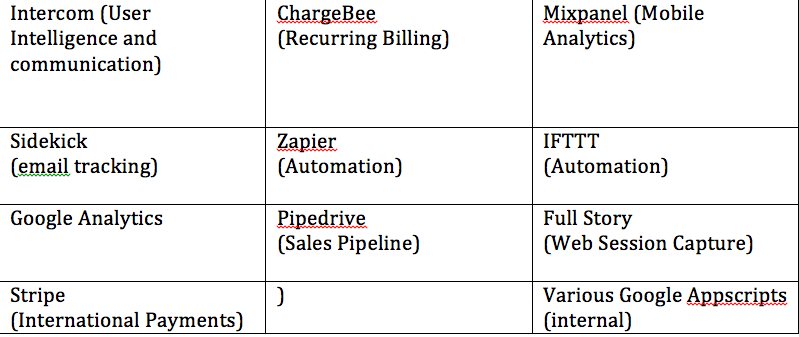
 Tools
Tools
These are the various tools used by the KiSSFLOW team and other participant companies who attended the roundtable
Conclusion
Very hard to summarize such a detailed session, but one parting thought stands out. Attention to details followed by automation and customization seems to be the way to go.