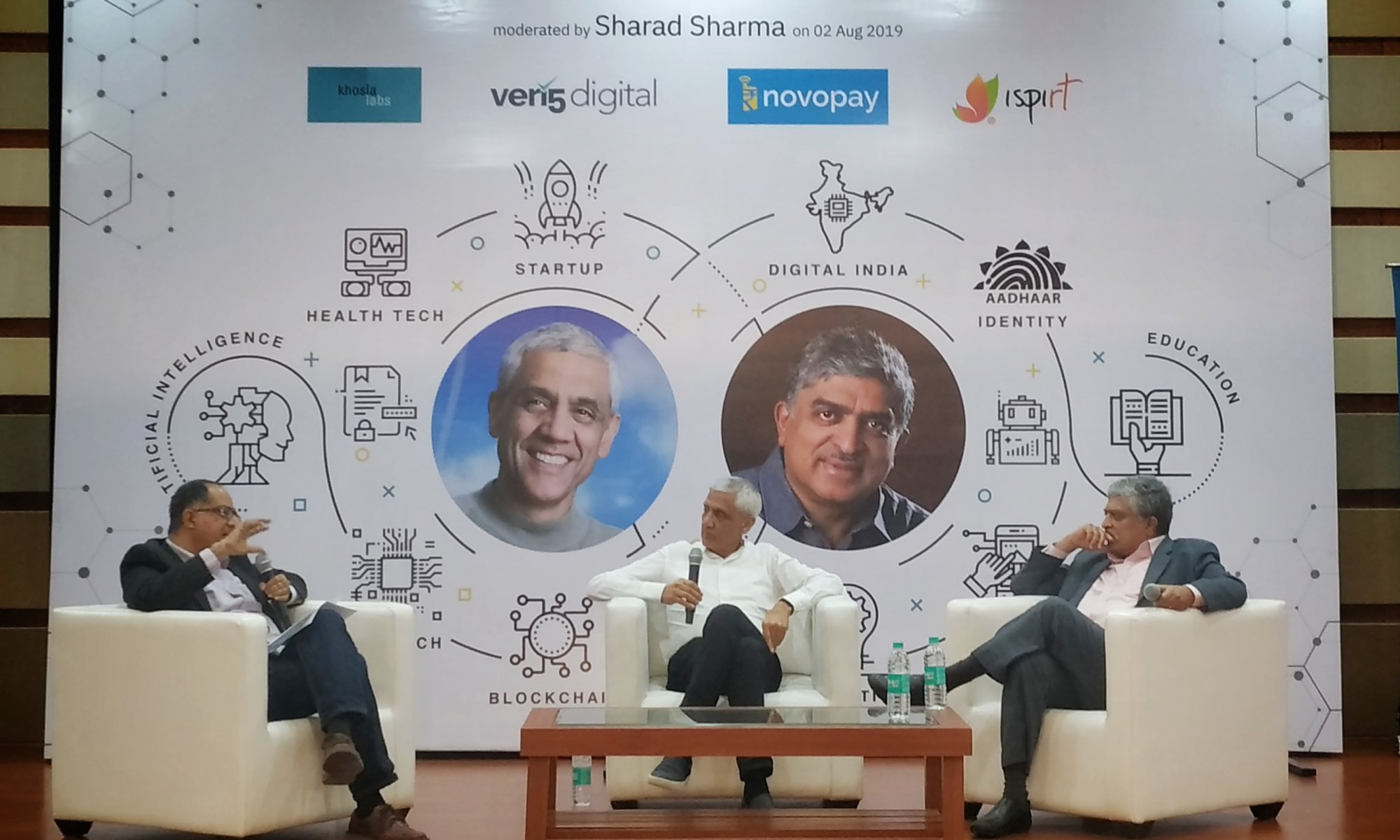
On a cloudy Bangalore evening on August 2nd, the otherwise quiet campus of a medical college in the ‘startup saturated hub of Koramangala’ was bustling with energy. That night the campus was hosting a fireside chat with Vinod Khosla (renowned Venture Capitalist and Co-Founder of Sun Microsystems) and Nandan Nilekani (Co-Founder of Infosys), with Sharad Sharma (Co-founder of iSPIRT) acting as moderator.
Sitting in the midst of many young entrepreneurs, Sharad remarked how energetic Vinod and Nandan are at their respective ages.
Vinod responded “I have this fear that you can grow old when you retire, not retire when you grow old. So, I hope I never retire. As long as you have interesting problems to work on, there’s nothing more exciting to do than work on that.”
Sharad commented that even after all of his accomplishments, it seems that Vinod sees himself as the David in a ‘David vs Goliath’-styled battle and wondered whether that was a fair assumption.
Vinod replied “You want to be the underdog. You want problems to be hard. If they were easy to solve, somebody would have solved them. The problems are very large when you look at them initially. If you apply exponential learning to that, you can catch up with any problem very quickly. If you get on the right path to exponential solutions, they’re not as hard as they seem. Just starting to solve the whole problem in one step is like trying to climb Mount Everest in one step and go straight to the top without going to base camp 1, base camp 2 along the way.”
Turning to Nandan, Sharad asked “I think India does not have a David vs Goliath mindset. Does it?”
Nandan replied “India didn’t get Independence without thinking big. India’s first elections is another example of thinking big. I think it’s all there. Now, we are applying it in new ways. We shouldn’t be daunted by the size of the problem. Whether you’re solving a small problem or a large problem, it requires the same amount of thinking. So, you might as well solve the large problem. There’s much more value for your time and money. Today, you’ve, on one side, an extraordinary array of things that need to be fixed. And, you have an extraordinary array of tools & technology that can fix those problems. You’ve access to enormous amounts of capital & great talent. There’s no better time than this”
Sharad brought the conversation back to Vinod, asking what it takes for entrepreneurs to step up to big problems, to unlearn, to position themselves to be breakthrough entrepreneurs.
Vinod expressed that, in his view, “most people, most of the time, are limited by what they think they can do, not what they can actually do. Most people limit themselves. It’s a surprising thing to say, but I almost always find it to be true.”
He elaborated that entrepreneurs must have the courage to take one little step at a time on this exponential climb. They do not have to figure out the whole journey in order to start the journey. They will determine the right paths to follow along the way. They just have to be creative in figuring them out.
He mentioned that he doesn’t mind failing and that his “willingness to fail gives [him] the ability to succeed. Most people fail to try, instead of trying and failing.”
He went on to share an observation with the audience. He said “I look back 40 years and I can’t find one major innovation that came from a large company. Not one. General Motors and Volkswagen couldn’t design an electric car. Boeing & Airbus couldn’t do space as SpaceX could. None of the media companies did media as Twitter and Facebook did. None of the Pharma companies did Biotechnology as Genentech did.”
It’s important to note that he mentions ‘large innovation’ and not ‘incremental innovation’. Also, he refers to innovations that turned out to be large in their impact on markets that they were meant for.
While there are many examples to support this claim, let’s take examples from the period of the early days of Sun Microsystems, about four decades ago.
Xerox’s PARC lab had a treasure trove of innovation that would have never seen the light of day, had it not been for Apple.
IBM at their research lab in mid-1970s, pulled together some of the smartest people in the field to create a functioning relational database system based on Ted Codd’s theory (Codd was an English computer scientist who, while working for IBM, invented the relational model for database management, which served as the theoretical basis for relational database management systems).
They succeeded and developed a functional language called SEQUEL (Structured English Query Language), later changed to SQL. In any sense imaginable, it was a breakthrough, but it wouldn’t have revolutionized the software industry had it not been for Larry Ellison’s Oracle.
Vinod mentioned that “when the path is not clear and you are inventing something new, almost certainly it would be a startup, despite how hard it may sound!”
He mentioned that when people in the energy sector looked to GE and Siemens to innovate, they didn’t.
In the current market dynamics with large tech monopolies, we see, at times, that an incumbent does well at copying what a startup does, but they rarely outdo the hunger and agility of a fast-growing startup. Google had trouble with the social network, and there are numerous examples to this effect. However, given the large distribution that few of the monopolies have with nearly zero marginal cost to acquire new customers, even if the product is not the best to be found in the market, some other inherent advantages can make a me-too product of a large incumbent thrive. For example, Microsoft, despite Slack’s rise and successful IPO, is doing well with Teams because it is leveraging its corporate-ubiquitous Office 365 suite. (Ending Q2 2019, Teams had 13 million DAUs as compared to Slack’s 10 million DAUs.)
These occurrences should in no way deter the entrepreneur, but he or she does need to immerse him or herself in systems thinking and order effects of multiple degrees when looking at how dynamics in the market that he or she is trying to disrupt, will evolve.
Following up on this point, Sharad pointed out that usually there is something working in the background enabling the entrepreneurs to carry out the change. The wind in their sails such as a technological shift, market change, and public goods.
He cited examples of GPS, India Stack and Solaris, (a UNIX operating system developed by Sun Microsystems) which came about as a result of AT&T and Bell Labs opening up UNIX standard to the world.
Nandan agreed and said “So far entrepreneurs’ successes have been built on huge investments in public infrastructure by governments like the Internet, GPS etc. We need to invest in long term digital infrastructure. Only governments can afford it or have that vision. Then open it for private innovation.”
He further mentioned that “It’s a philosophy that we have adopted in India. Just as the US invested in the internet, GPS etc, we will invest in identity, payment infra, etc. and API-fy them, thus allowing innovation to happen on top of that.”
Vinod chimed in saying that “almost all entrepreneurs build on things that are already there. In fact, how much you orient that infra towards entrepreneurial ventures makes a huge difference. There are lots of startups in the US-based on government funding in science and technology in US universities.”
Nandan added that the advantage that we have now, is that the technology has been democratized. “We have all kinds of open source stuff. We have a cloud. It’s all there and it’s all free. And it’s for entrepreneurs to take that and mix & match. That’s where we can do a lot of work.”
Sharad summarized this exchange aptly by saying that “solving hard societal problems needs ‘jugalbandi’ between public infrastructure and private innovation on top of it.”
Taking an another IBM example of how this ‘jugalbandi’ manifests, while IBM was working on SEQUEL, a group of professors at the University of California, Berkeley, were also working on a relational database as part of a project called ‘Project Ingres’, funded by the US Government. Oracle used both as a foundation to spear through the market.
It was ultimately the speed of execution that saw Oracle making headway, utilizing the nudge given to it (IBM introduced a commercial product in February 1982, despite having a relational database up and running in 1977. They also were invested in hierarchical database system called IMS and were not fast enough to cannibalize their product)
In India, if the BHIM app was a B2C reference implementation of UPI, PhonePe utilized the opportunity to build a massive business on top of the same UPI stack.
Shifting gears, Sharad recalled his interaction with Jeff Bezos where he said Jeff takes just 10 minutes to determine whether a new hire is a good fit or not and one of the key things he looks for while assessing, is resilience. Entrepreneurs need loads of it as a ‘David’
Sharad asks Vinod about what he looks for in an entrepreneur when he is deciding whether to fund a start-up.
Khosla said “There’s no one formula. As a tech investor, you’re looking for a unique solution where one can create an advantage over time. It’s as simple as that. The biggest ingredient is the quality of the team you assemble. If it’s a great team, we will fund it, whether it has an interesting business plan or not. Team matters the most. And then how clever you are, how differentiated your technology is, how far ahead are you of others in thinking through how you want to build it.
“An important characteristic when evaluating somebody who has failed is what’s their rate of learning. That’s probably the most important way you evaluate an entrepreneur. When they move from job to job, do their teams follow? What books do they read? Do they spend their time learning new things? There are half a dozen things like that, that I personally use in evaluating people. But it’s still the hardest thing you do.”
He further added that he also has a strong belief that people with expertise in the area apply old rules and old biases while noting that experience is one of the largest biases there is!
Taking his Fintech investments as examples, he explains how the founders of Square, Stripe and Affirm never had worked in Fintech. Not knowing the space proved to be a massive advantage, and the entrepreneurs tried to solve problems with great empathy towards the customer, iterating while operating with first principles thinking.
He added by giving the example of Elon Musk’s never having worked in the auto industry prior to founding Tesla. Automakers laughed at the Silicon Valley startup with no experience in auto-making. He made lots of mistakes but fixed them quickly while figuring out a better way to proceed than those decided through conventional wisdom.
For those looking to innovate in their existing field of expertise, Sharad echoed that unlearning is more important than learning.
Sharad posed a nuanced question for Vinod by asking whether a healthcare start-up hiring a VP of Sales should hire one from the healthcare sector or not. Sticking to his view, Vinod remarked that he would rather hire an athlete who would be innovative and learn quickly instead of someone with bias from experience!
Talking about the quantum of funding and the excess in Silicon Valley, Vinod said, “nobody can say what’s the right level of money. It feels like a lot of money is floating around in Silicon Valley. But that’s because there’s been a lot of really good ideas. When new platforms emerge, new applications become possible. Then great entrepreneurs build them.”
He continued, “if you look at your mobile phone, and the touch interface, there really hasn’t been a huge startup in the US in the last five years. If you look at Uber, Lyft, Airbnb, Pinterest, they are all done. We have to see where are new platforms coming along.”
When prodded on what these new platforms can be, he elaborated “I do think AI is a new platform and offers lots and lots of opportunity. Fortunately, other than ads, it offers opportunity in lots of societal impactful areas. Medicine is my favourite. 3D printing is another new platform that people aren’t using enough. One of my favourite startups right now is trying to 3D print whole houses. What’s the advantage of that? Much, much lower cost, 24 hours to print a house, but more importantly, it’s environmental footprint is much better.”
He also wanted to highlight for entrepreneurs that large problems to be solved are not confined to the domain of software, but are present in many other fields as well, such as food, construction, healthcare, transportation, etc., which are all open to radical innovation.
He said that when one merges biotechnology solutions, such as CRISPR, with AI, all kinds of disease solutions are possible. He also believes that startups will dominate drug discovery using AI, far more than the big pharmaceutical companies will.
He brought up the example of Impossible Foods and recalls everyone asking him why he was investing in a hamburger company.
Giving the rationale behind the investment, he said that “about 30% to 40% of the planet’s land surface area is used for animal husbandry of one sort or another. I think about 90% of it could be freed up if the same meat was produced using the techniques like Impossible Burger. Plant proteins are the best way to save the planet. It’s healthier than meat proteins for humans because they come with cholesterol and other negative things. So it’s a beautiful solution.”
Talking more about the funding and its quantum, he argued that “the more money you raise initially, the less likely you are to succeed. There’s some beauty & elegance in very small amounts of money because it forces you to think about your problem much harder…you’re much more creative with your solution.”
While speaking about the need for creativity, Sharad mentioned that when entrepreneurs hit an obstacle during the process, they need to re-imagine and rejig, however, there are certain components that ought not to be rejigged, such as the core set of company values.
He gave examples of Infosys and Wipro being built on that value-based culture while noting that Bangalore’s vibrant ecosystem today is definitely a beneficiary of that culture.
Nandan agreed and said “values are very important if we want to build companies to last. If we want to build companies that sustain themselves over decades and really have an impact on society and the world, they have to be anchored in a core set of values.”
Vinod concurred, reflecting that “if you don’t have values, the first time you run into a problem, people scatter. If you have values & you have a mission, people stick together & double their efforts as a team. Values play a big role during bad times”
Following this topic, the chat naturally steered towards how entrepreneurs evaluate risk and what can be the right framework for evaluation and mitigation.
Vinod said that there is no one set of rules and that everyone has their own way of looking at it.
He added, “most investors reduce risk to the point where the probability of success is high, but its consequences of success are inconsequential. It’s a good way to get a predictable rate of return. I personally find it much more exciting, where the probability of success is low, but consequences of success are consequential.”
He gives the example of Larry and Sergey, founders of Google, saying that they had no interest in making a billion dollars when Yahoo offered to acquire them. They wanted to be consequential and change the world.
While this statement is accurate, it is important for us to study the different risk scenarios that entrepreneurs face, as well as how they frame and mitigate them. The reason is that while the Google founders rejected a billion-dollar offer, they also badly wanted to sell ‘PageRank’ to AltaVista and Yahoo for 1 Million Dollars to go back and resume their studies at Stanford (from The Google Story by David A.Vise).
So then, the question that arises is that how do the founders have different outlook towards acquisition at different points in time? What changes in-between, what transitions entrepreneurs go through, and what indicators should they rely on? One can dive into ‘Prospect theory’ and other frameworks for decision analysis under risk, but we also need to consider the passion and hunger of entrepreneurs, the unquenchable fire that powers them through the risk. That will have to be another iSPIRT blog altogether!
Speaking about the risk entrepreneurs face, Nandan added “You need a social fabric which delinks failure from the person; which recognizes that failure is a tremendous experience which is likely to increase the probability of success the next time around. Here failure, person & institutions are entwined.”
————
Talking about AI, Vinod said “There will be enough jobs for humans after ‘Artificial General Intelligence. We don’t have enough humans for all the elder care we need and all the childcare. We could deploy ten times as many people and raise better children and look after elders much better. Those are just two examples. I think relationships are the inherent human tendency that will not go away and meaning will come from relationships.”
Nandan added that “the assumption that AI will automate everything and there will be no jobs left and therefore we need UBI and a way to keep them occupied is wrong. The way I think about it, AI amplifies human capability. The combination of human and AI is going to be very strong.”
As the chat drew to a close, it became more apparent than ever that for the Indian ecosystem to thrive and for us to build massive companies, we need a new entrepreneur archetype – the kind that can zoom out and look at macro-trends, applies ‘systems and first principles’ thinking, platform over product thinking, have big audacious goals while being extremely empathetic to their customers.
There used to be a long gestation period from the founding of a company until it faced foreign competition on Indian soil. From early days of MakeMyTrip, Naukri to Ola, Quikr a few years back, it has reduced drastically such that companies like PhonePe have to ward off heavyweights like Facebook, Google and Amazon within a year of starting up! Indian entrepreneurs will need to buckle up as the platform wars on Indian Playground with digital public goods will only intensify, unleashing massive opportunities and growth for the country.
Please write into [email protected] for a deep dive and information on upcoming iSPIRT events where we will discuss this new entrepreneur archetype as part of what we call ‘Athletic Gavaskar Project’, and to learn more about our volunteer model.







 In this polytheistic world of entrepreneurs, who is the Startup Initiative for? If it’s for all the various types of entrepreneurs, then it will quickly succumb to the 80% syndrome. Policy-makers will address things that are the common denominator for all types of entrepreneurs. While this is necessary , it’s not sufficient. As any product manager in the technology industry will tell you, this 80% fix is a recipe for failure.
In this polytheistic world of entrepreneurs, who is the Startup Initiative for? If it’s for all the various types of entrepreneurs, then it will quickly succumb to the 80% syndrome. Policy-makers will address things that are the common denominator for all types of entrepreneurs. While this is necessary , it’s not sufficient. As any product manager in the technology industry will tell you, this 80% fix is a recipe for failure. Each of these types of entrepreneurs is in pain today . Last year 54% of the funded technology startups redomiciled themselves outside India. This year, iSPIRT estimates, the exodus has accelerated and the number of companies redomiciling out of India will be
Each of these types of entrepreneurs is in pain today . Last year 54% of the funded technology startups redomiciled themselves outside India. This year, iSPIRT estimates, the exodus has accelerated and the number of companies redomiciling out of India will be  Entrepreneurship is a state of mind
Entrepreneurship is a state of mind