Access to formal credit continues to be one of the largest challenges faced by MSMEs in India due to lack of verifiable data about their business.Digital payments data combined with GST data has the potential to unlock millions of SMEs & bring them into the formal system. India is going through a Cambrian explosion of data usage. It is estimated that the monthly data consumption on every smartphone in India is estimated to grow nearly five times from 3.9 GB in 2017 to 18 GB by 2023 as per a report by Swedish telecom gear maker Ericsson.
Picture Source: Digital Desh
As businesses and their processes get digitized, it provides us a unique opportunity to re-imagine credit products for MSMEs like never before.
In order to move from traditional Asset-based lending to Data based lending it is important to make the following design considerations:
- Underwriting based on Data – Assess creditworthiness in real time based on the consented data provided by the user
- Low-Value – Bringing down the cost of processing a loan using digital platforms like eKYC, eSign & UPI enables one to process sachet sized loans
- Smaller Tenures – Offer small tenures to reduce risk and thereby build better credit history of a customer
- Customised Loan Offers – In the old world, loan products were designed to be one size fits all; With data & better underwriting, create a “loan offer on the fly” for a borrower based on his need
Getting started with GST Data Based Lending – Basics
- Over 8M+ businesses in India will file GST returns
- Every invoice in the GSTN system is verified by the counterparty
- GST returns are digitally signed and this data can be accessed through consent of a small business
To access this data, you need the understand the three types of GST APIs:
- Authentication – Allows a taxpayer to login into his GST account from any application
- Returns – Allows a taxpayer to file his returns from any application
- Ledger – Allows a taxpayer to view & share his tax data with any application
You can access the GSTN Sandbox & APIs here: bit.ly/GSTAPIs
If you want more insights, do join the GSTN Discussion Forum here: bit.ly/GSTgroup
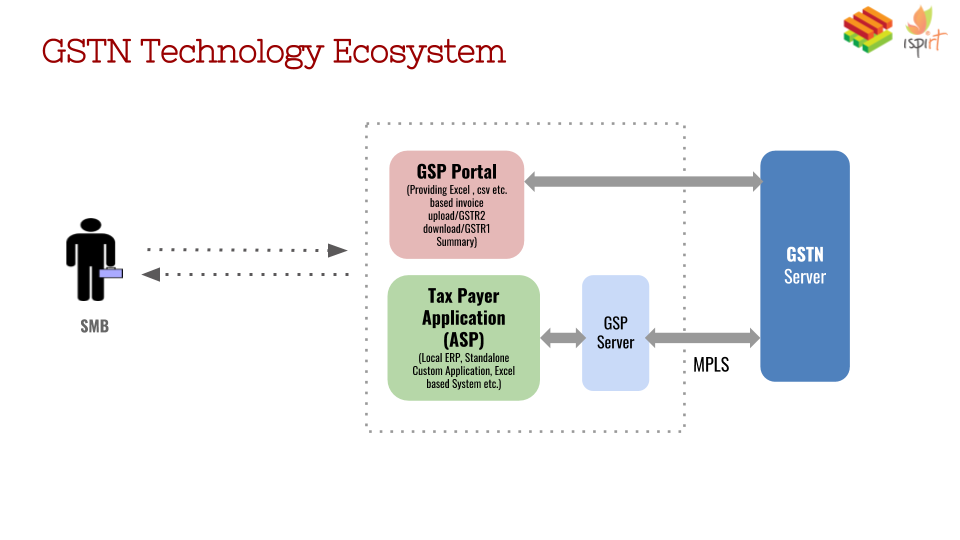
The GSTN Tech Ecosystem
Goods and Service Tax Network is a section 8 company set up to provide common and shared IT infrastructure and services to the Central and State Governments, Tax Payers and other stakeholders for the implementation of the Goods & Services Tax (GST).
In this context, it is important to understand the below two roles of GSTN:
- Direct portal for taxpayers – https://services.gst.gov.in/services/login
- Expose APIs thru GSPs (GST Suvidha Provider) – http://www.gstn.org/gsp-list/
GST Suvidha Provider (GSP) – Companies which provide GST API Gateway as a service to application service providers; They are appointed by the GSTN and list of the GSPs can be accessed here:http://www.gstn.org/gsp-list/
ASPs – Companies which provide the user interface for business to file or fetch their returns from the GSTN
Naturally, ASPs are a great fit as distribution partners for lending as they own and control the end user experience of small businesses. Some of the examples are:
Accounting Software Providers
-
- They help small business manage their accounting, inventory & even payroll;
- They have rich data sets about the small business including their GST returns Eg: Tally (Desktop), Zoho/Cleartax/Profitbooks (Cloud-based)
Tax Filing Software Providers
-
- These companies help business who use excel/manual billing/custom software to prepare their GST return & file it every month;
- One of the key stakeholders here is the accountant who essentially is the business advisor for an SMB and tapping into them as an influencer channel is a great opportunity Eg: Cleartax, SahiGST etc.
Supply Chain Automation Companies:
-
- Today many FMCGs and Large manufacturing companies are using software to track their sales/inventory in their supply chain; For e.g: Asian Paints, Tata Steel, ITC etc.
- As these companies enable a large of wholesalers, retailers to use their software problem, there is a great opportunity to extend credit to their entire ecosystem
- Eg: Moglix, Channel Konnekt, Bizom etc.
Example of a Lender – ASP Partnership
- Consider a services-based company which provides advertising services to multiple companies
- Let’s assume they use an accounting software like for example Cleartax or Zoho
- In the software, the SMB sees a one-click credit button (This is enabled through an integration with the ASP & lender)
- In a few clicks, the SMB is able to share multiple types of data like – GST, Payroll, Balance Sheet, Bank Statement etc. with the lender
- With consent, the lender uses this data for underwriting, build a credit score and makes a credit offer to the SMB
- The SMB provides his bank account details for real-time loan disbursement and based on the type of the business you can complete KYC
- Take mandate either digitally or physically based on the customer for repayments
There are various other data sources one could use to improve the underwriting like – Smartphone, Payments Data from the Bank, Bill Payments, Electronic Toll Collection & various others. Algorithms can use these data sources along with other other public data sets like – Seasonal demand for a product, Import/Export, GDP, Consumption Patterns to do contextual lending.
We recommend you go through the presentation above to understand these basics & do watch the pre-recorded webinar session below on How to Leverage GST data for Flow-based lending for more details.
At iSPIRT, we are working with multiple stakeholders to create a winning implementation of Flow-Based Lending. Do watch out for future announcements from us for entrepreneurs working in this space or write to us [email protected] to know more.
About the Author
Nikhil Kumar is a full-time fellow with iSPIRT Foundation, a non for profit think-thank and has been focussed on building the developer ecosystem for the India Stack.
Twitter: @nikhilkumarks