The Design RoundTable last week lead by Deepa Bachu and Rajan, was not what I expected. By and large, design to me was either a part of an application (UI / UX) or a concept which i did’nt know much about. But, when we went in depth with Deepa, I realized that design is an integral part of who we are and what we see around us.
Through detailed discussions, we were made to think about what design is and what design meant to individuals, communities, startups as well as our customers. The first task started with a a simple question, what is design? One can come up with several ways to describe it and the audience described it as – Design is something that solves a need, brings convenience, humanizes products (i.e. bringing human touch to products), explores empathy, understands customers and is about continuous learning. What stood out for me was that design is all about Love and passion in order to bring out the best products/services to address a customer need, in a manner that creates value with ease and convenience. This would enable the users to be at ease and fall in love with what it represents. If a design is thought through with love, compassion and empathy, the user’s journey and experience improves.
The first task in the workshop was to work in a group and explore design features (good vs. bad designs) both within and outside a room. This enabled us to look at things from a design lens. The group came up with very interesting insights of how people dry their clothes in modern buildings differently from those who dry clothes on their balconies or how badly the electric poles in India are designed or how cobbled streets are an interesting design element than traditional tar roads.
 This experience made us understand and be aware of the small and subtle difference between good and bad design. I was able to realize and conclude how crucial it is to be empathetic to customer needs and when, where and how they experience a product / service. Hence, it is essential to understand things from the customer’s perspective which eventually helps us improve the utility of the product and services that one offers.
This experience made us understand and be aware of the small and subtle difference between good and bad design. I was able to realize and conclude how crucial it is to be empathetic to customer needs and when, where and how they experience a product / service. Hence, it is essential to understand things from the customer’s perspective which eventually helps us improve the utility of the product and services that one offers.
This applies to all our products and services. We are all trying to build a product around enhancing the customer experience and thinking through each aspect from the users point of view is crucial. How does a user discover your product or hears about you? How do you ease the process of sign ups? How important is the design of your website or application? What does the product do for the customers and what are the benefits of it? These are just few examples of how we can think from the customer’s point of view. By allowing ourselves to think from the customer’s perspective, we are enabling us to re-imagine the product and user’s journey through various channels to engage and enrich with the user.
Another interesting insight was around humanizing products as consumers are humans. Adding a human touch to design can make an experience great. For example, addressing consumers in emails by their names or to have a real person to sign off at the end of an email.
There were many other aspects we covered in our conversations. We discussed the importance of elegance in design and a belief that “UI without UX is Superficial”. We also discussed the importance of creating that WOW factor or customer delight in making customers your brand ambassadors. For creating customer delight, one has to first answer what benefits a customer will get and how one can create customer experience through positive emotion. The combination of these simple three stage processes will help us to think through the various customer delight experiences that we can design.
Another tool that Deepa spoke about and is quite helpful is an Empathy Map. It is a 2×2 matrix to understand the journey of a customer. Four questions need to be asked.
1) What do customers say about your product,
2) What do they do while experiencing your product,
3) What are they thinking while they use the service and
4) How do they feel over all.
This is an experiment which should be done periodically with various sets of customers which can make each member of the team sensitive to the customer journey. An interesting point learnt is that every time we have an insight on one of the four touch points — Say, do, think and feel , we could use this as a starting point. For example, while booking a flight online, how is the customer journey when they first login, are they looking for the cheapest price if so what do they say about that experience, what do they think while looking for the cheapest price (will they get the cheapest price on this website and will the price change later) and what do they feel (lets pay it by it before it changes).
By following some basic templates we can rethink our products and imagine the customer journey in a manner that we could live it on a daily basis. The love / empathy towards our customers, which results in benefits for the customer and eventually helps in designing the WOW (delight) moments are what makes a lasting impact and creates a bond between the brand and the customers.
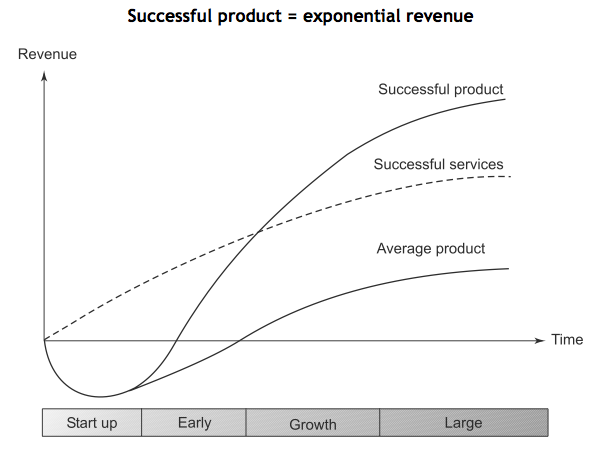
Hence, design is one of the main pillars of building a successful product and I hope we all can make design an integral part of the organization. Our thinking should bring compassion and love to customers through Design.
Thank you Deepa and Rajan for wonderful session on Design thinking
Deepa is a design and product leader who most recently worked at Intuit as the Director of Design and Product Management. Deepa’s passion is to transform customers’ lives by creating products that solve their biggest unmet needs.
Deepa has 20 years of experience in the Tech industry where she has played a variety of roles across Product Development, Experience Design, Product Management and General Manager. Deepa’s experience has given her expertise in creating and taking global products for both emerging markets as well as developed markets across multiple domains.
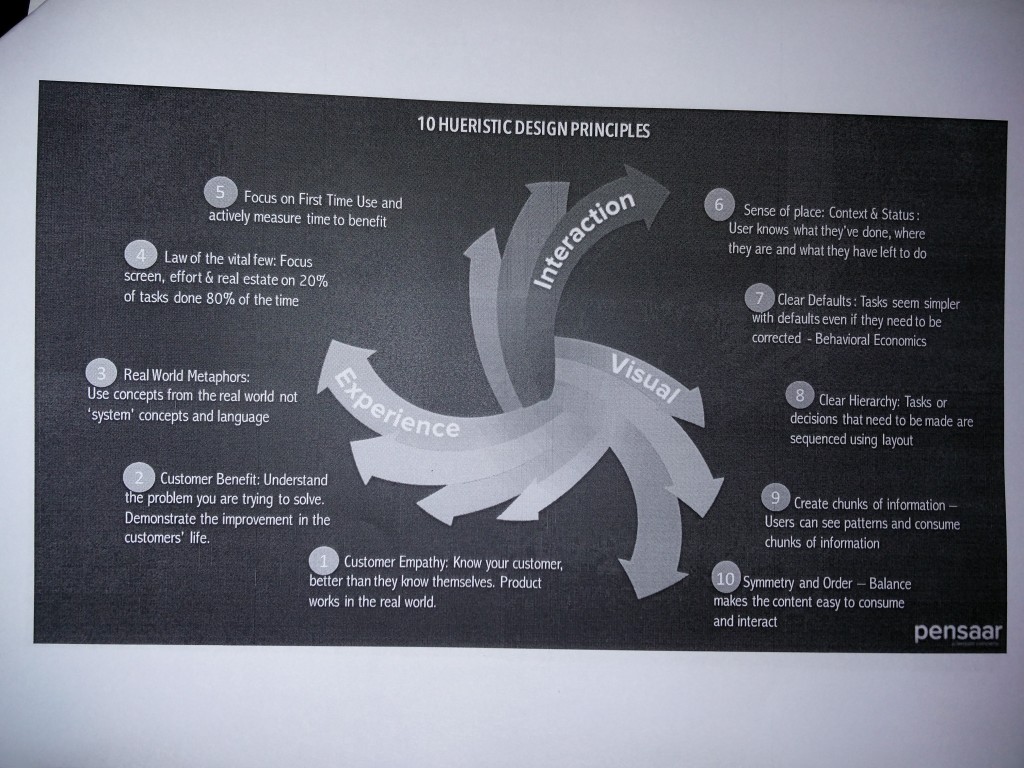
What is Design (Iteration 1)

What is Design (Iteration 2)

What is Design (Iteration 3)

What is design iteration4 ?


Guest post by Gaurang Sanghvi