I see 3 shifts critical for me!
Taking a line from the popular Brown Bear children’s book, I believe that our SaaS startups have a real opportunity to leverage some leading shifts in the global SaaS evolution. While there are many areas of change – and none less worthy than the other – I am highlighting 3 shifts for SaaS (tl;dr) which our entrepreneurs can actually work with and help change their orbit:
- Market shifts with AI/ML for SaaS to build meaningful product & business differentiation,
- Platform Products shift to transform into a multi-product success strategy,
- Leveraging Partnerships for strategic growth and value co-creation.
Some background
I joined iSPIRT with a goal to help our community build great global products. I believed (and still do) that many entrepreneurs struggle with the basics of identifying a strong value proposition and build a well thought out product. They need strong support from the community to develop a solid product mindset & culture. My intent was to activate a product thinkers community and program leveraging our lean forward playbooks model.
I had several conversations with community members & mavens on playbooks outcomes and iterating our playbook roundtables for better product thinking. I realized that driving basic product thinking principles required very frequent and deeper engagement with startups. But our playbooks approach model – working in a distributed volunteer/maven driven model – is not set up to activate such an outcome. Through our playbooks model, our mavens had helped startups assimilate best practices on topics like Desk Sales & Marketing, something that was not well understood some years back. This was not a basic topic. The power of our playbook RTs was in bringing the spotlight on gaps & challenges that were underserved but yet highly impactful.
As a product person, I played with how to position our playbooks for our entrepreneur program. I believe our playbooks have always been graduate-level programs and our entrepreneurs are students with an active interest to go deep with these playbooks, build on their basic undergraduate entrepreneurship knowledge, and reach higher levels of growth.
The product thinking and other entrepreneurial skills are still extremely relevant, and I am comforted by the fact that there are many community partners from accelerators like Upekkha to conclaves like NPC and event-workshop formats like ProductGeeks which are investing efforts to build solid product thinking & growth skills.
As the SaaS eco-system evolves, and as previous graduate topics like desk sales & marketing are better understood, we need to build new graduate-level programs which address critical & impactful market gaps but are underserved. We need to help startups with meaningful & rapid orbit shifts over the next 2-3 years.
Discovering 3 Shifts for SaaS
Having come to this understanding I began to explore where our playbooks could continue to be a vibrant graduate-level program and replicate our success from the earlier playbooks. Similar to an entrepreneur’s journey, these three shifts became transparent through the many interactions and explorations of SaaS entrepreneurs.
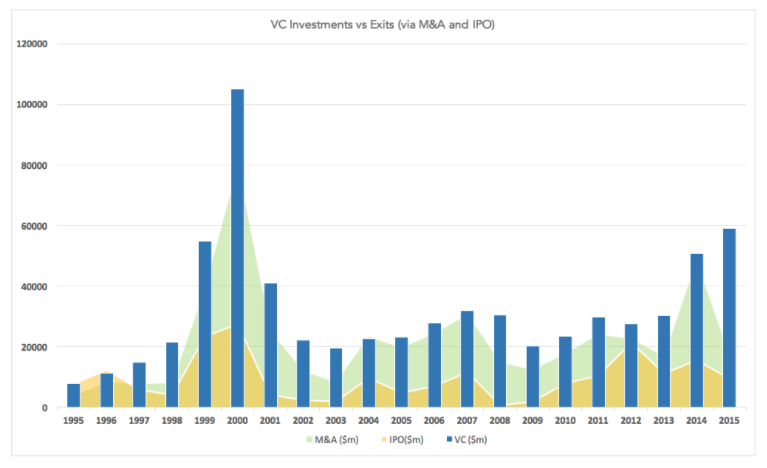
Market Shift with AI/ML for SaaS

There is no doubt that AI is a tectonic shift. The convergence of big data availability, maturity of algorithms, and affordable cloud AI/ML platforms, has made it easy for SaaS startups to leverage AI/ML. During a chance roundtable learning session on Julia with Dr. Viral Shah & Prof Alan Edelman, it was clear that many entrepreneurs – head down into their growth challenges – were not aware of the realities behind the AI hype. Some thought AI/ML should be explored by their tech team, others felt it required a lot of effort & resources. The real challenge, however, is to discover & develop a significantly higher order AI-enabled value to customers than was feasible 2 years ago. While AI is a technology-driven shift, the implications for finding the right product value and business model are even greater.
As I explored the AI trend I saw a pattern of “gold rush” – build a small feature with rudimentary AI, market your product as an AI product… – making early claims with small changes which do not move the needle. It became clear that a step-by-step pragmatic thinking by our SaaS startups was required to build an AI-based leapfrog value proposition. This could help bring our startups to be at “par” and potentially even leap ahead of our global brethren. Here was an opportunity to create a level playing field, to compete with global players and incumbents alike.
To validate my observations, I did quick small research on SaaS companies outside of India on their approach with AI. I found quite a few startups where AI was already being leveraged intrinsically and others who were still trying to make sense. Investments varied from blogging about the AI trend, branding one as a thought leader, to actually building and delivering a strongly differentiated product proposition. E.g.:
- Chargebee rivals Stripe & Recurly, are experimenting with ML for fraud detection and for predicting subscription cancellation.
- InstaSafe (cyber security for cloud) rivals Centrify, OneLogin… have been researching AI for authentication & security.
- SignEasy rival DocuSign acquired Appuri for integrating ML into their product value.
- Nintex and AgilePoint are exploring how engaging ML bots will help understand and improve processes in the BPM space.
There are no successes, yet! Our startups like Eka, Wingify, FreshWorks, WebEngage… have all been experimenting with AI/ML, stumbling and picking themselves up to build & deliver a higher level of value. Some others are setting up an internal playground to explore & experiment. And many others are waiting on the shore unsure of how to board the AI ship.
How do we enable our companies to create new AI playgrounds to analyze, surface, validate and develop higher order customer values & efficiencies? To chart a fruitful journey with AI/ML there are many challenges that need to be solved. And doing it as a group running together has a better chance of success.
The AI+SaaS game has just begun and it is the right time for our hungry entrepreneurs to Aspire for the Gold on a reasonable level playing field.
Shift to Platform Products
 As market needs change, the product needs a transform. As new target segments get added different/new product assumptions come into play. In both these scenarios existing products begin to age rapidly and it becomes important for startups to re-invent their product offerings. To deal with such changes startups must experiment and iterate with agility. They require support from a base “internal” platform to allow them to transform from a single product success strategy to scaling with multiple products strategy.
As market needs change, the product needs a transform. As new target segments get added different/new product assumptions come into play. In both these scenarios existing products begin to age rapidly and it becomes important for startups to re-invent their product offerings. To deal with such changes startups must experiment and iterate with agility. They require support from a base “internal” platform to allow them to transform from a single product success strategy to scaling with multiple products strategy.
This “internal” base platform – an infrastructure & layout of technology components to interconnect data & horizontal functional layers – would help to build & support multiple business specific problem-solution products (vertical logics). The products created on such a platform provide both independent as well as a combined value proposition for the customers.
Many startups (Zendesk, Freshdesk, Eka, WebEngage…) have undertaken the painful approach of factoring an internal platform to transform their strategy & opportunity. Zoho has been constantly reinventing itself and launching new products on a common platform, some of which are upending incumbent rivals in a very short period of time. WebEngage transformed itself from a “tool” into an open platform product.
“As the dependency on our software grew, customers needed more flexibility to be able to use their data to solve a wide range of business problems…significant difference in the way we build products now. We have unlocked a lot of value by converting ourselves into an open platform and enabling customer data to flow seamlessly across many products.” – Avlesh Singh, WebEngage
The effort to build an internal platform appropriately architected to support growing business needs (many yet unknown) is non-trivial and requires a platform thinking mindset for increased business development. It must be architected to allow rapid co-creation of new & unique product values in collaboration with external or market platforms. This can help the startup be a formidable player in the growing “platform economy”.
Leveraging Potential Strategic Partnerships
 A strategic partner offers 2 benefits for startups. First is the obvious ability to supercharge the startup’s GTM strategy with effective distribution & scale. How does one make a strategic partnership? Pitching to a strategic partner is very different from pitching to a customer or investor. PSPs look for something that is working and where they can insert themselves and make the unit economics even better.
A strategic partner offers 2 benefits for startups. First is the obvious ability to supercharge the startup’s GTM strategy with effective distribution & scale. How does one make a strategic partnership? Pitching to a strategic partner is very different from pitching to a customer or investor. PSPs look for something that is working and where they can insert themselves and make the unit economics even better.
“I thought I knew my pitch and had the details at my fingertips. But then I started getting really valuable, thought-out feedback…I had to focus on pitching to partners, not customers.” – Pallav Nadhani, FusionCharts
The second leverage with a partner is the ability to innovate in the overlap of the partner’s products & offerings and the startup’s product values. A good partner is always looking for startups which can co-create a unique value proposition and impact an extremely large customer base.
“…we still have only three four percent market share when it comes to customers. So if we have to participate we have to recognize that we are not gonna be able to do it alone we’re going to have to have a strategy to reach out to the entire marketplace and have a proposition for the entire marketplace…you need to (do it) through partnerships.” – Shikha Sharma, MD Axis Bank
Both these partnership intents if nurtured well can bring deep meaningful relationship which can further transcend scale into a more permanent model (investment, M&A…).
Working with the 3 Shifts of SaaS
While each shift is independent in its own importance, they are also inter-related. E.g. an internal platform can allow a startup to co-create with a partner more effectively. Partners are always interested in differentiated leading-edge values such as what is possible with leveraging AI/ML. Magic is created when a startup leverages an internal platform, to co-create a strong AI-enabled value, in the overlap & gap with potential strategic partners.
And that’s what I see
I see a vibrant eco-system of SaaS startups in India working on creating leading global products. Vibrancy built on top of the basic product thinking skills and catapulted into a new orbit by navigating the 3 shifts.
“Reading market shifts isn’t easy. Neither is making mindset shifts. Startups are made or unmade on their bets on market/mindset shifts. Like stock market bubbles, shifts are fully clear only in hindsight. At iSPIRT, we are working to help entrepreneurs navigate the many overlapping yet critical shifts.” – Sharad Sharma, iSPIRT
Through our roundtables, we have selected six startups as the first running group cohort for our AI/ML for SaaS playbooks (Acebot, Artoo, FusionCharts, InstaSafe, LegalDesk & SignEasy).
If you are hungry and ready to explore these uncharted shifts, we are bringing these new playbooks tracks for you.
Please let us know your interest by filling out this form.
Also, if you are interested in volunteering for our playbook tracks, we can really use your support! There is a lot to be done to structure and build the playbook tracks and the upcoming SaaSx5 for these shifts for SaaS. Please use the same form to indicate your support.
Ending this note with a sense of beginning, I believe that our startups have a real opportunity to lead instead of fast-follow, create originals instead of clones. They need help to do this as a running group instead of a solo contestant. It is with this mission – bring our startups at par on the global arena – that I am excited to support the ProductNation.
I would like to acknowledge critical insights from Avlesh Singh (WebEngage), Manav Garg (Eka), Shekhar Kirani (Accel Partners), Sharad Sharma (iSPIRT). Also am thankful for the support from our mavens, volunteers & founders who helped with my research, set up the roundtables, and draft my perspective with active conversations on this topic: Ankit Singh (Wibmo/MyPoolin), Anukriti Chaudhari (iSPIRT), Arvi Krishnaswamy (GetCloudCherry), Ganesh Suryanarayanan (Tata GTIO), Deepa Bachu (Pensaar), Deepak Vincchi (JuliaComputing), Karthik KS (iSPIRT), Manish Singhal (Pi Ventures), Nishith Rastogi (Locus.sh), Pallav Nadhani (FusionCharts), Praveen Hari (iSPIRT), Rakesh Mondal (RakeshMondal.in), Ravindra Krishnappa (Acebot.ai), Sandeep Todi (Remitr), Shrikanth Jangannathan (PipeCandy), Sunil Rao (Lightspeed), Tathagat Varma (ChinaSoft), Titash Neogi (Seivelogic), and many other volunteers & founders.
All images are credited to Rakesh Mondal
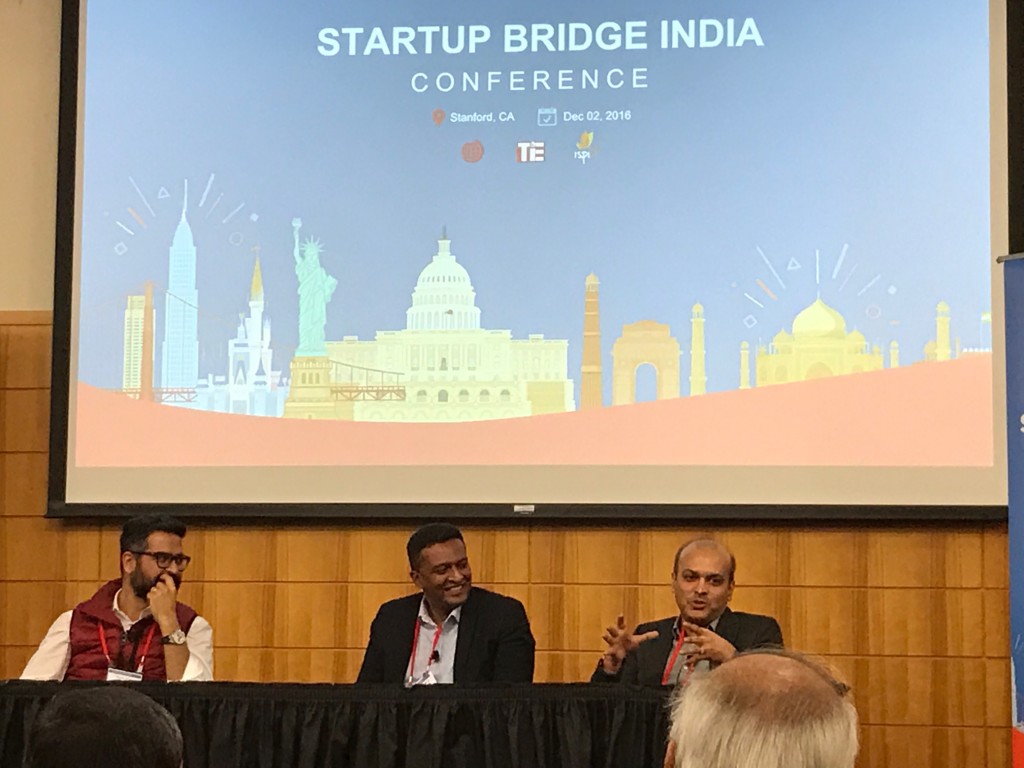





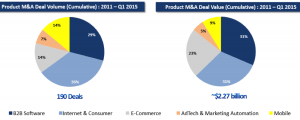
 For one, it was the first step in breaking down borders between Silicon Valley and India. It is no easy feat to gather the top BD and Corp Dev executives from the largest tech Silicon Valley giants all together under a single roof. But with representatives from 65 corporates meeting 28 startups driving 120 connections for partnerships and investment/acquisition discussions, the very fact that the doors were opened, some even knocked down, was a giant leap for the ecosystem.
For one, it was the first step in breaking down borders between Silicon Valley and India. It is no easy feat to gather the top BD and Corp Dev executives from the largest tech Silicon Valley giants all together under a single roof. But with representatives from 65 corporates meeting 28 startups driving 120 connections for partnerships and investment/acquisition discussions, the very fact that the doors were opened, some even knocked down, was a giant leap for the ecosystem.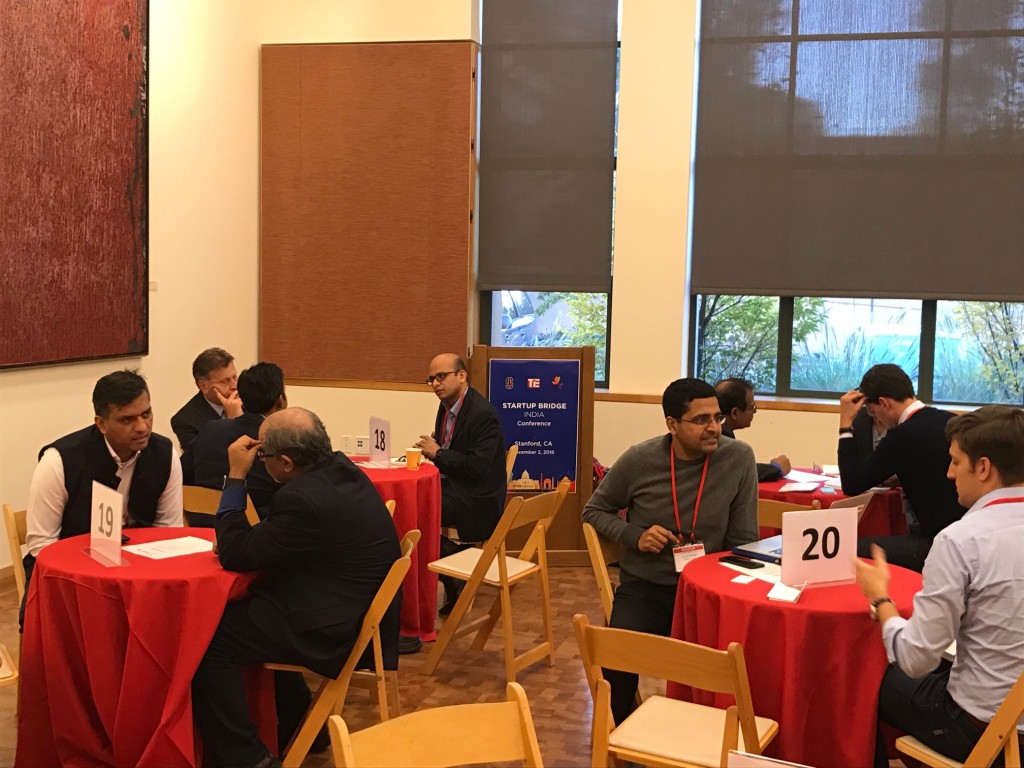 StartUp Bridge India, with an NPS of 68%, was another valiant step towards putting the Indian startup ecosystem on the global map alongside mammoths like the US and Israel. Team Indus, an Indian startup working to land a rover on Mars, is India’s literal moonshot. Startup India, working to increase cross-border investments and M&A, was India’s figurative moonshot. And after Startup Bridge, it was clear, that this moonshop has a robust arm and is gaining an increasingly powerful momentum.
StartUp Bridge India, with an NPS of 68%, was another valiant step towards putting the Indian startup ecosystem on the global map alongside mammoths like the US and Israel. Team Indus, an Indian startup working to land a rover on Mars, is India’s literal moonshot. Startup India, working to increase cross-border investments and M&A, was India’s figurative moonshot. And after Startup Bridge, it was clear, that this moonshop has a robust arm and is gaining an increasingly powerful momentum. 






 On January 23, 2015, the
On January 23, 2015, the  After an interactive session with Neeraj, we had a candid discussion with the Corporate Development attendees about their experiences acquiring Indian startups. The Yahoo and Twitter corp dev folks shared the key learnings from their recent M&As in India. Here are some takeaways for us in the Indian software product industry and for the next acquirers of Indian startups:
After an interactive session with Neeraj, we had a candid discussion with the Corporate Development attendees about their experiences acquiring Indian startups. The Yahoo and Twitter corp dev folks shared the key learnings from their recent M&As in India. Here are some takeaways for us in the Indian software product industry and for the next acquirers of Indian startups:
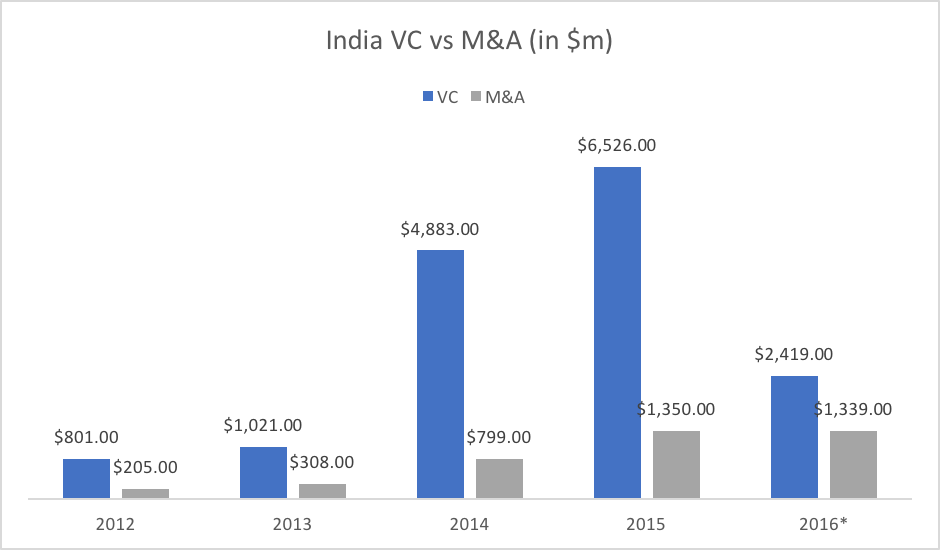
 Many key aspects such as taxation (especially in the context of Singapore), seed funding, liabilities, ease of the process, ESOP and stock plans need to be considered, while deciding the location of incorporation .
Many key aspects such as taxation (especially in the context of Singapore), seed funding, liabilities, ease of the process, ESOP and stock plans need to be considered, while deciding the location of incorporation . Some basic Q&A
Some basic Q&A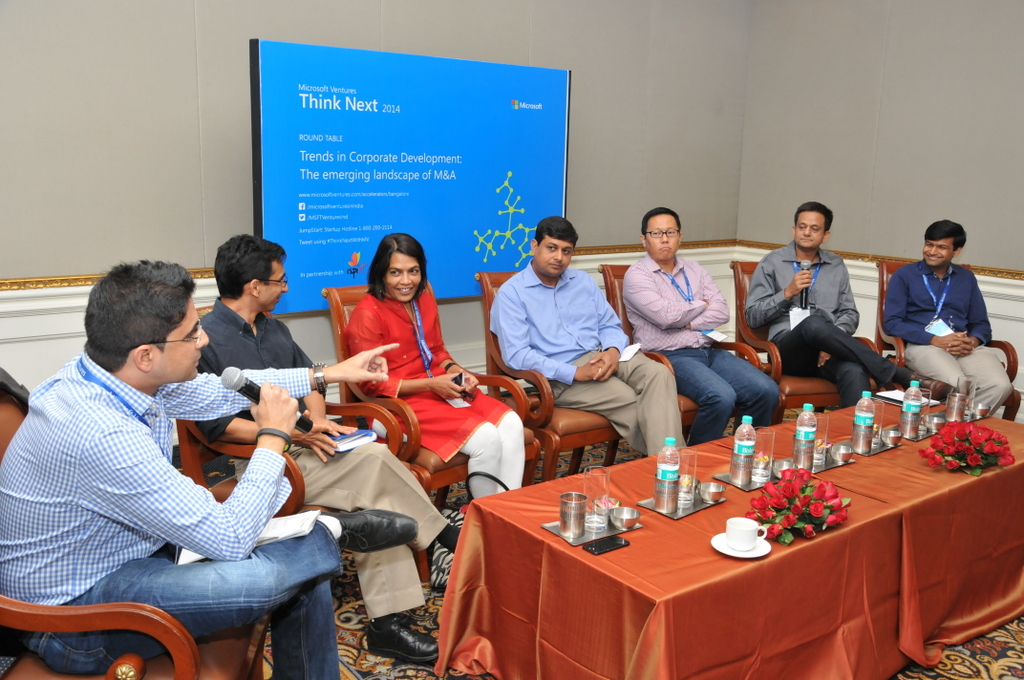 Last Friday, I hosted the M&A Panel at
Last Friday, I hosted the M&A Panel at 
