An Indian software company serving majorly clients in the US or Europe is not an unusual thing anymore. However, if anybody were to guess the location of the India office, a company that counts amongst its clients about 100,000 small businesses globally, they would most probably chose Bangalore or Hyderabad. However, Appointy, which is an advanced web-based scheduling software tool and has around 90,000 salons, spas, and dance and yoga classes as its clients in 100 countries does it out of Bhopal. Similarly Kayako, which sells support software to over 30,000 clients including NASA, Peugeot, Sega found its roots in Jalandhar, which as per their own website is “one of the least likely places to establish a technology start-up”.
The emergence of these companies from relatively smaller towns, highlight India’s comparative advantage in terms of ability to build high quality companies in the domain of Software as a Service (SaaS). The inherent model of the SaaS business does not require proximity to the end user. In the simplest terms, it is a software that can be accessed through a web browser, by paying a subscription, either on a monthly or yearly basis. The software is hosted exclusively by the provider, as opposed to being downloaded upon purchase and subsequently hosted by the client. The customer gains by spending less upfront, not having to maintain hardware and not worrying about upgrades & data security. Driven by such factors, the SaaS model is growing exponentially and the global market for 2015 stood at USD 31 billion (NASSCOM). The growth is expected to continue at CAGR of 18% to reach a market size of USD 72 billion by 2020. Another study by Google and Accel Partners estimates the 2020 market to be USD 132 billion.
The Indian SaaS landscape is expected to evolve even faster. The FY16 market is estimated to be USD 407 million, a 34% growth over FY15. This figure is expected to triple by 2020 growing at a CAGR of 27%, 1.5 times the global growth rate. It is easy to see why India is going to be a hotbed of activity for SaaS companies. The cost of product developers is one of the biggest items in a SaaS company’s P&L Statement. A software developer in India costs 25% of what a similarly skilled one based in the US would cost. India has an estimated 36,000 product managers, 25,000 SaaS engineers and 100,000 other engineers with the skills for building a SaaS product. Another critical factor is the adoption of mobiles as the primary device for accessing data. India being a mobile-first nation is well placed to ride this shift as its young companies are more flexible and can focus on mobile platforms.
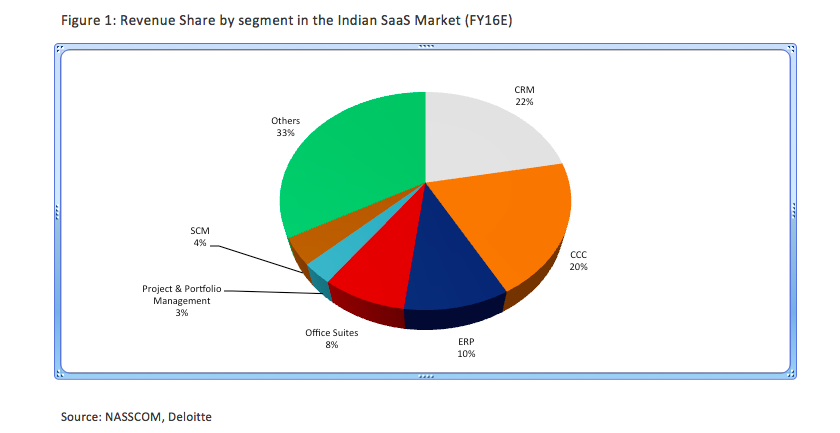
Buoyed by these advantages, companies have been sprouting in every segment of the sector. NASSCOM estimates that there are around 150 Indian companies offering SaaS solutions. 40% of these companies have been incorporated after 2010. Customer Relationship Management (CRM), Content Collaboration and Communication (CCC) and Enterprise Resource Planning are the hottest segments accounting for more than half the market in FY16.
Growth in the domestic market is also expected to be a major boost factor for the Indian companies. A deeper dive into the key underlying sectors which are adopting SaaS brings even more attractive prospects to the fore. Healthcare, E-commerce, BFSI and education sectors have been the most targeted segments by emerging SaaS companies. Each of these sectors is expected to expand at a healthy pace in the near future riding on the overall economy’s consumption led growth. At 7.6%, India’s GDP growth rate for FY16 has been the highest in the last 5 years. Small and Medium sized businesses emerging in these sectors would be much more nimble and receptive of SaaS solutions to avoid upfront large capex on technology.
The investor community, financial and strategic, has also embraced the SaaS opportunity with both hands. A total of USD 650 million was invested in SaaS companies in India till 2014. The funding in 2014 is estimated to be between USD 170 million to USD 200 million. However, the funding skyrocketed in 2015 with USD 450 million in the first half of the year itself. Some of the most active investors who are backing SaaS companies India are as below.
- Accel Partners (Freshdesk, Hotelogix, Mobstac, Mindtickle, Chargebee, Zettata,)
- Blume Ventures (Zipdial, Hotelogix, Mettl, FrameBench, WebEngage, Mobstac)
- Nexus Venture Partners (Druva, Indix, Unmetric, TargetingMantra, Genwi, Helpshift)
- Norwest Venture Partners (BlueJeans, CRMnext, Act-On, Capillary Technolgies, Attune)
- Sequoia Capital (Druva, Capillary Technologies, Knowlarity, Practo)
The investors will have their hands full the short to medium term as most of the companies move traverse from Series A to B to C and so on. With companies maturing and cash balances building up, the sector is also expected start throwing up M&A opportunities much faster than any other sector.
The SaaS story hasn’t quite meant curtains for the traditional software licensing business model yet. Currently, SaaS commands only about 9% of the over Indian software market which is estimated to be USD 3.1 billion. However, Indian SaaS companies have already been able to create a market perception of building great products at lower cost. Currently, a large number of Indian SaaS companies would lie in the revenue range of USD 1 to 2 million. However, there are enough cases of rapid scaling up companies (such as Freshdesk, Capillary Technologies and CRMNext) to help us believe that we will soon see companies with multiple billion dollars in revenue emerging from India.
 This is a guest post by Arvind Yadav, Executive Team Member at Aurum Equity Partners LLP.
This is a guest post by Arvind Yadav, Executive Team Member at Aurum Equity Partners LLP.











 The venue was at Chennai (Mahabalipuram) well described by above tweet and event started with afternoon session by Pallav Nadhani of FusionCharts on Referral Marketing. The discussion started emphasizing needs of marketing starts before existence of the product and continues with product and marketing should not be looked in silos away from the product. One question for SaaS founders is whether their startups are geared to leverage product features to perform self-marketing of the product The session brought some real examples of SaaS firms who have already done this successfully.
The venue was at Chennai (Mahabalipuram) well described by above tweet and event started with afternoon session by Pallav Nadhani of FusionCharts on Referral Marketing. The discussion started emphasizing needs of marketing starts before existence of the product and continues with product and marketing should not be looked in silos away from the product. One question for SaaS founders is whether their startups are geared to leverage product features to perform self-marketing of the product The session brought some real examples of SaaS firms who have already done this successfully. People who teared down choose right words to share comments to the founder who offered his product for tear down, also adding kind words “Do not become defensive. Their inputs are to improve not to criticize”. SaaS founder in the audience really liked the positive impact of product Tear Down session and followed with asks to #ispirit to have more startups in Product Tear Down sessions and suggestion for virtual Product Tear Down session.
People who teared down choose right words to share comments to the founder who offered his product for tear down, also adding kind words “Do not become defensive. Their inputs are to improve not to criticize”. SaaS founder in the audience really liked the positive impact of product Tear Down session and followed with asks to #ispirit to have more startups in Product Tear Down sessions and suggestion for virtual Product Tear Down session. One strategy is using the “powered by *product logo*” inside the product to attract more prospects. This was especially used in a novel way. WebEngage chose a customer (of course, after a due diligence) to sell its low-priced product in an unpresent geography. Then the logo was added in the product to attract more customers in the region. The customer acquisition cost is reduced as a result. Nemesh of Appointy (which helps businesses to schedule appointments) has 118,000 customers, all of them acquired at zero cost of marketing. This was done through backlinks (two lines of codes in the product), which would indirectly show up in the Google search when someone searched for a tool for appointments. Ankit spoke of four strategies to customer acquisition without much marketing spend.
One strategy is using the “powered by *product logo*” inside the product to attract more prospects. This was especially used in a novel way. WebEngage chose a customer (of course, after a due diligence) to sell its low-priced product in an unpresent geography. Then the logo was added in the product to attract more customers in the region. The customer acquisition cost is reduced as a result. Nemesh of Appointy (which helps businesses to schedule appointments) has 118,000 customers, all of them acquired at zero cost of marketing. This was done through backlinks (two lines of codes in the product), which would indirectly show up in the Google search when someone searched for a tool for appointments. Ankit spoke of four strategies to customer acquisition without much marketing spend.
 CRM for Startups:
CRM for Startups:


 Ever wondered if a Software could help business chart the next growth curve?.
Ever wondered if a Software could help business chart the next growth curve?.