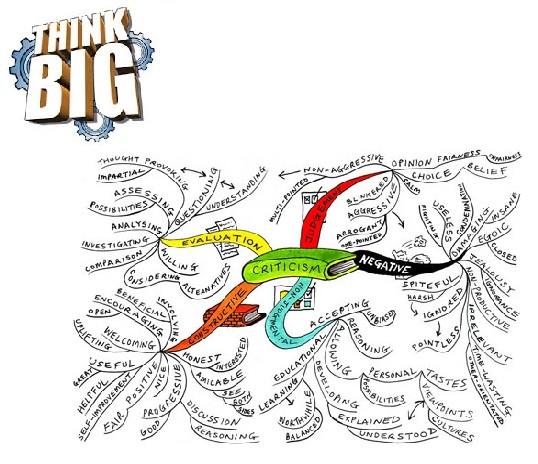
Seems only apt to summarize our 12 learning’s on 12-12-12
#1 – ‘Kitna detee hai’ ?
Maruti car runs a campaign in India around “keetna deti hai” (means in local language – how much mileage will i get in?). The first question on the applicant’s mind was – post program will I get a better pay or shift into a company of my dreams. Very few (23% of them to be precise) reported that learning is more important to them than placement assistance.
My take – People seem to forget that getting inside is easier than staying & growing inside. On the bright side its good that we have companies willingly wanting to hire the first batch immediately on graduation.
#2 – “Code Centric to Customer Centric”
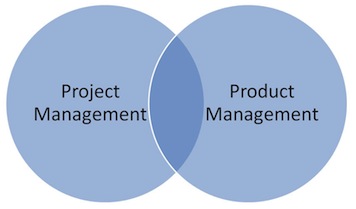
The idea of transitioning from being technology centric to customer centric does seem to resonate the most with individual participants who cited “Project Management to Product Management” as the #1 desired transformation – to be able to understand the customer and the business context of what they are already doing.
My take – Business programs can only be valuable if they accelerate that transformation. Knowledge dissemination cant be the driver!
#3 – “Badge is important”
The idea of getting a diploma or a degree is rather important as a take away from the program. Brand is clearly important.. Interestingly enough compared to “Guaranteed Career Path” this was voted lower though.
My take – With liberal badge printing machines in the country most hiring managers see through it and at best use as a filtering criteria.It is even less valuable for senior R&D professionals
#4 – “Have you done this before?”
Surprisingly (at least to us) companies who wanted to nominate people to the program asked this question more often than the participant themselves. Companies (both senior HR/L&D & Engineering leaders) as well as participants appreciated the fact that the curriculum is relevant and faculty is world class but the risk appetite for companies seemed to be lower than participants who pledged nominations for the “next” batch!
My take – first movers almost always benefit. That’s why the early bird gets the worm. The program’s pilot batch will have the best foot forward to establish a brand and move the offering to higher price points for next batch.
#5 – “Better seat at the table”
Most R&D leaders showed frustration around why they were not able to add value with their global partners and wanted to equip themselves with the right knowledge and immersions to be able to have a better seat at the table and enjoy broader responsibilities.
My take – unless people make an effort to understand the productizing process all those frustrations will continue to rise. Intent and ability to help are two different things!
#6 – “I don’t want to become a Product Manager”
Interestingly enough not all senior R&D managers (64%) wanted to learn the “business” & “customer” context to become a Product Manager, instead they wanted to differentiate themselves and build a better career path on the Product Engineering Leadership track with the role models being cited as CTO and Head of R&D.
My take – Product Management as a process should be everybody’s business to understand, playing the role of a real Product Manager not so much as it’s a harder role to play than one thinks!
#7 – Its better if its hard to get in
The moment they heard that only 20% of applicants will be selected to the program the value of the program went up by a factor of 2 (Price to Value Analysis)
#8 – Relevance of MBA to their Product Leadership Growth
Majority of the Product Professionals who had done their MBA from Top B-schools cite around 21% of the subjects/topics being relevant to them in their current role. 35% of them believe that the degree gave them the necessary break/promotion/new role.
My take – General Purpose MBAs (even from top B schools) are great for people who don’t know what they want in life and hence want to get the exposure to HR, Finance, Operations, Marketing etc. Institute’s Board have actually factored this in and designed the curriculum to map to industry’s expectations.
#9 – Influence Building skills are missing
Across 5 categories of the curriculum, leadership skills were rated 3rd most desired after Customer Connect & Insights and User Experience & Product Innovation. Within leadership skills leading by influence was ranked higher than other soft skills like negotiation, presentation, cross culture communication and conflict resolution.
My take – One’s Influentiality Index (II) is actually the biggest propeller for career path acceleration, functional skills for an average R&D product professional is actually fairly high.
#10 – Relevance is good but I want my exec education to be personal
Relevance of the program resonated overwhelmingly with the target audience but most also desired personal mentoring 1:1 with industry execs and a personalized leadership development plan with necessary psychometric assessments. Interestingly 92% have never gone through such personalized assessment at their company.
My take – I wish I had done assessments like MBTI, DISC, Product Leadership Influentiality Index (PLII) etc to really know my gaps and build a plan to bridge them faster as opposed to rely on accidental growth.
#11 – Free money – take it or not take it?
Several industry reports suggest that 26% of educational tuition reimbursement budgets goes underutilized with global R&D centers in India. Most (97%) desired to get tuition reimbursement from their company to pay for the program, however it dropped to 52% the moment it was disclosed that only self sponsored candidates will be offered placement assistance.
My take – With retention being the driver for some companies to sponsor education this is bound to happen..
#12 – Scaling Startups vs Large Companies
Management teams from both groups desire better product leaders (91% – Agree + Strongly Agree) however their approach of solving is starkly different. Global R&D Centers want a longer program (underlying theme being retention) vs Scaling Startups want a menu of courses to select from.
Would love to hear your thoughts – especially if you are a product professional wanting to accelerate your career path with atleast 8 years of experience or part of the exec management team who wants to develop strong product leaders in the India R&D center! More info at www.productleadership.in