This is an exciting occasion for our indigenous software industry as India’s National Policy on Software Products gets rolled out. This policy offers the perfect framework to bring together the industry, academia and the government to help realise the vision of India as a dominant player in the global software product market.
For ease of reference, let us summarise some of the major things that the policy focuses on
- Single Window Platform to facilitate issues of the software companies
- specific tax regime for software products by distinguishing them from software services via HS code
- enabling Indian software product companies to set off tax against R&D credits on the accrual basis
- creation of a Software Product Development fund of INR 5000 crores to invest in Indian software product companies
- grant in aid of INR 500 Crores to support research and innovation on software products
- encouragement to innovation via 20 Grant Challenges focusing on Education, Healthcare & Agriculture thus further enabling software products to solve societal challenges
- enabling participation of Indian software companies in the govt. e-marketplace to improve access to opportunities in the domestic market
- developing a framework for Indian software product companies in government procurement.
- special focus on Indian software product companies in international trade development programmes
- encouraging software product development across a wide set of industries by developing software product clusters around existing industry concentrations such as in automobile, manufacturing, textiles etc.
- nurturing the software product start-up ecosystem
- building a sustainable talent pipeline through skilling and training programmes
- encouraging entrepreneurship and employment generation in tier II cities
- creating governing bodies and raising funds to enable scaling of native software product companies.
There is good cause for cheer here. The policy offers to address many of the needs of the Software Product Ecosystem. For the first time, HS codes or Harmonised Codes will be assigned to Indian software product companies that will facilitate a clear distinction from ‘Software Services’ facilitating availing of any benefits accruing under the ‘Make in India’ programme. In addition, this will enable Indian software product companies to participate in govt contracts through registration on GeM (Govt. eMarketplace).
Considering that we remain a net importer of software products at present, steps such as the inclusion of Indian software products in foreign aid programmes, setting up of specialised software product incubators in other geographies and promoting our software product capabilities through international exhibitions definitely show intent in the right direction. With a commitment to develop 10000 software product start-ups, with 1000 of them in tier II cities, technology entrepreneurs building IP driven product companies can now look forward to infrastructural and funding support. The policy also aims to go beyond metro-centric development with a commitment to develop tech clusters around existing industry concentrations, enable skilling and drive employment in non-metros and tier II cities while actively encouraging Indian software companies to solve native problems.
This policy could not have been possible without the vision of the Honourable Minister Shri Ravi Shankar Prasad, and continuous engagement and discussions with Shri Ajay Prakash Sawhney, Rajeev Kumar and Ajai Kumar Garg from MEITY and their team.
We have seen software companies solving native problems do exceptionally well, just look at what Paytm has been able to achieve while driving digital payments in India. There is now an understanding ‘Make in India’ can help us bridge the digital divide given that Indian entrepreneurs have a greater understanding of local issues and the challenges that are unique to us.
Setting up bodies such as the National Software Products Mission in a tripartite arrangement with the industry, academia and govt. to enable creation and monitoring of schemes beneficial to native software product companies is another much-needed step that will create a forum distinct to our software product companies and help give them a strong voice.
We would like to thank Lalitesh Katragadda, Vishnu Dusad, Sharad Sharma, Rishikesha T Krishnan, Bharat Goenka, T.V. Mohandas Pai, Arvind Gupta for their diligent efforts on the continuous dialogue and inputs for the policy.
While launching the policy is a great start, its implementation is what we all will have our eyes on. Now is the moment of action. We all look forward to fast-tracking of the various proposed measures under this policy for the benefits to start showing!
Website link to the official policy – (https://meity.gov.in/writereaddata/files/national_policy_on_software_products-2019.pdf)
References
JANUARY 15, 2019 – https://tech.economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/internet/india-needs-to-win-the-software-products-race/67533374
DECEMBER 8, 2016 – https://pn.ispirt.in/what-to-expect-from-draft-national-policy-on-software-products/
NOVEMBER 13, 2016 – https://pn.ispirt.in/national-software-policy-2-0-needed/
MAY 10, 2016 – https://pn.ispirt.in/taxation-and-digital-economy/
APRIL 29, 2016 – https://pn.ispirt.in/saas-the-product-advantage-and-need/
JULY 16, 2014 – https://pn.ispirt.in/government-recognizes-the-software-product-industry/
DECEMBER 11, 2013 – https://pn.ispirt.in/three-waves-of-indian-software/
JULY 16, 2013 – https://pn.ispirt.in/smbs-and-indian-software-product-industry-intertwined-fortunes/
JULY 4, 2013 – https://pn.ispirt.in/8-truths-why-it-services-organizations-cannot-do-software-products/











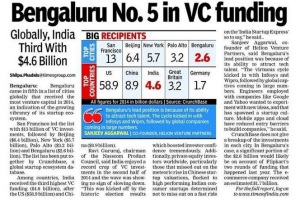
 For software products, destination is Bangalore, where many across the country migrate for an aspiring career in software, considered as silicon valley of india. Especially with the software product startup momentum, Bangalore is certainly the place for the ecosystem. Other locations such as Hyderabad and Pune are the other smaller hubs catching up in this front. In the global context, its bay area or seatle in US, the land where amazing software products have been made or being made.
For software products, destination is Bangalore, where many across the country migrate for an aspiring career in software, considered as silicon valley of india. Especially with the software product startup momentum, Bangalore is certainly the place for the ecosystem. Other locations such as Hyderabad and Pune are the other smaller hubs catching up in this front. In the global context, its bay area or seatle in US, the land where amazing software products have been made or being made.