India, a large country with a lot of geographical and economic diversity, faces interesting challenges with last-mile connectivity for internet users. PM-WANI programme provides a powerful technical and policy framework towards the goal of broadband proliferation across the country.
iSPIRT Foundation has been involved with the PM-WANI programme right from its inception. Dr Pramod Varma, Siddharth Shetty and other volunteers, were involved with the technical framework for unbundling the internet access and ensuring interoperability among all participants
As of date, the Centre for Development of Telematics (CDoT) and Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI) has been ably managing the mantle with all aspects related to the PM-WANI framework.
The PM-WANI has a unique, distributed and unbundled architecture. It has the following participants:
PDO – Set up and maintain the access point (AP). Users connect to this AP to access the internet.
PDOA – Provides the technical backend for the PDO for Authentication, Authorization and Accounting (AAA). PDOA provides a facility for the PDO operator to define broadband sachet for their users (e.g. 1GB data for Rs 5). PDOA also stores the users’ usage data as per the government security compliance.
App-Provider – Operates a mobile application for PM-WANI. A user will use this mobile application to discover a PM-WANI-compatible network. The App-Provider maintains the user KYC.
Central-Registry – It maintains the details of every registered PDO, PDOA and App-Provider. It is generally used to validate requests made between the participants.
PM-WANI facilitates the delivery of broadband access to users using PDO-operated WiFi access points (AP). A telecom/internet service provider provides the backhaul internet to this AP.
Instead of needing multiple licences and compliances to commercially distribute internet, in PM-WANI’s case, the PDO requires absolutely no compliance or licence to distribute internet locally!
That does not mean the security is compromised in any way. The user KYC is handled by the App-Provider and the usage logs are maintained by the PDOA
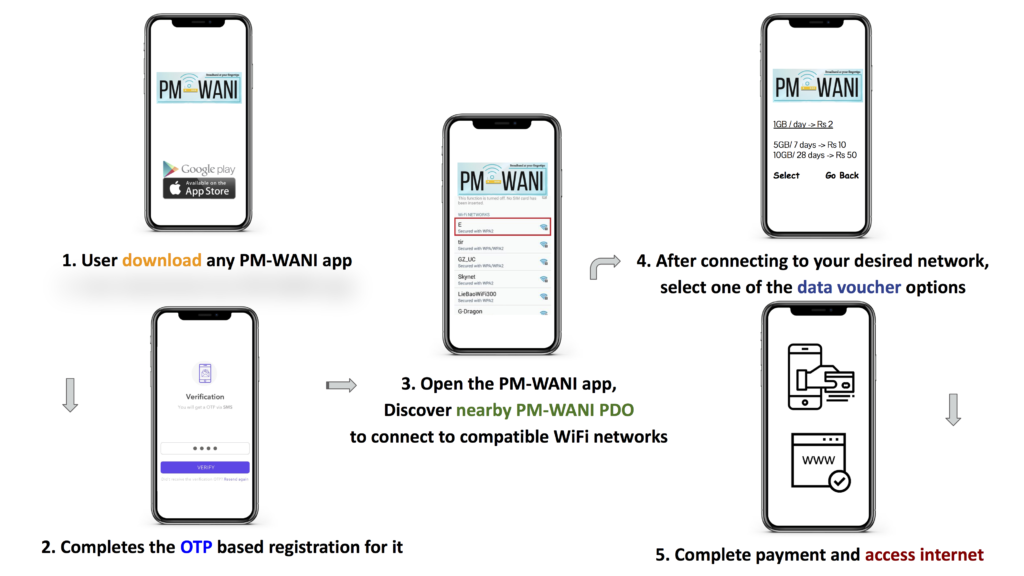
User Flow
PM-WANI as an earning opportunity for small entrepreneurs
This programme offers great monetary opportunities for entrepreneurs. Multiple companies are coming up with varied plans for becoming a PDO / PDOA. Let us discuss some of them
Case 1: Become a PDOA with a C-DoT software stack and onboard PDOs
This is for entrepreneurs to start their own PDOA business and create a network of PDOs (on their own or onboarding other small-business owners)
The Centre for Development of Telematics (C-DoT) provides a complete PDOA software stack as Platform as a Service(PaaS). Here, it takes care of all the technical requirements (including software, server and regulatory requirements). This enables entrepreneurs to start their PDOA operations without getting into the technical nitty-gritty. They charge a very low fee of Rs. 15000 for 3 months.
Costs
Here is the cost breakdown for a PDO for Year 1:
| Annual Internet pricing – 50 Mbps connection | Rs.600/month = Rs 7200/- |
| Annual Electricity & Router Maintenance | Rs.150/month = Rs 1800/- |
| Indoor AP which is CDoT PM-WANI compliant (WAYU) | Rs. 5300/- |
| Total Investment for year 1 for a PDO | Rs. 14300/- |
Cost breakdown for a PDO Year 2 onwards:
| Annual Internet pricing – 50 Mbps connection | Rs.600/month = Rs 7200/- |
| Annual Electricity & Router Maintenance | Rs.150/month = Rs 1800/- |
| Indoor AP which is CDoT PM-WANI compliant (WAYU) | Already Purchased |
| Total Investment from year 2 onwards for a PDO | Rs. 9000/- |
In this business case, we consider that 95% of the voucher collection goes to the PDO and 5% goes to the PDOA
The annual investment for the PDOA is Rs. 60000
Value Proposition for PDO
A PDOA can create an excellent value proposition for a PDO using this model.
We have considered the average voucher cost for a user to be Rs 2, Rs 5, Rs 10 and Rs 15., eg. a user will buy an internet sachet/voucher of Rs. 2 for 1GB data a day.
The below table shows the cost-benefit analysis for Year 1 wherein a PDO charges Rs 2 per voucher. Annually, PDO breaks even with just 20 daily users and achieves 100% return-on-investment (ROI) with just 40 daily users in the first year itself! Year 2 onwards it’s just 13 users to break even and 25 users for 100% ROI.
PDO Year 1
| Daily Cost Per User(in Rs) | No of daily users for breakeven | No of daily users for 100% ROI |
| 2 | 20 | 40 |
| 5 | 8 | 16 |
| 10 | 4 | 8 |
| 15 | 3 | 6 |
PDO Year 2 onward
From year 2 onwards, the ROI starts getting even sweeter as the operating cost further reduces to Rs. 9000 for a year
| Daily Cost Per User(in Rs) | No of daily users for breakeven | No of daily users for 100% ROI |
| 2 | 13 | 25 |
| 5 | 5 | 10 |
| 10 | 3 | 5 |
| 15 | 2 | 4 |
Value Proposition for PDOA
The below graph shows the number of PDOs needed to be deployed for a PDOA to break even for different voucher costs and daily users
Case 2 – Become a PDO with other private players
There are quite a few companies that allow people to deploy their own PDO directly. They provide a PDO infrastructure (AP and allied software) for Rs 12000 a year
Costs
Here is the cost breakdown for a PDO:
| Annual Internet pricing – 50 Mbps connection | Rs.600/month = Rs 7200/- |
| Annual Electricity & Router Maintenance | Rs.150/month = Rs 1800/- |
| AP which is PM-WANI compliant | Rs. 12000/- |
| Total Investment for year 1 for a PDO | Rs. 21000/- |
Value Proposition for PDO
| Daily Cost Per User(in Rs) | No of daily users for breakeven | No of daily users for 100% ROI |
| 2 | 29 | 58 |
| 5 | 12 | 24 |
| 10 | 6 | 12 |
| 15 | 4 | 8 |
PM-WANI Challenges
Interoperability
One of the major challenges that PM-WANI is facing right now is protocol compliance. Because of this, some of the PM-WANI Apps do not work interoperably with the PDO.
Example: A PM-WANI app developed by company A is not compatible with a PDO of company B. A’s app only works with A’s PDO
Data Sharing
The protocol, as of now, does not have a standard way to share usage data between the participants. Hence, the app provider does not get any incentive when a user buys a PDO/PDOA coupon due to this lack of data sharing. Also, for implementing roaming between PDOs, it is essential that there is some data-sharing standard available between multiple PDOAs.
Grievance Redressal
This is another area that is not regulated at the moment
What iSPIRT is up to
We are working on multiple fronts to solve the PM-WANI challenges.
For the interoperability issue, we are developing a certification mechanism for PM-WANI that cthe PDOA or App-Providers can easily usewith minimal complexity.
We are developing a reference implementation for PM-WANI. The community can further build on it and come up with more interesting business models for PM-WANI.
We are also working on proposals for improving the protocol to address the challenges mentioned in the previous section.
Please feel free to write to Saurabh Chakrabarti at [email protected] for any questions.