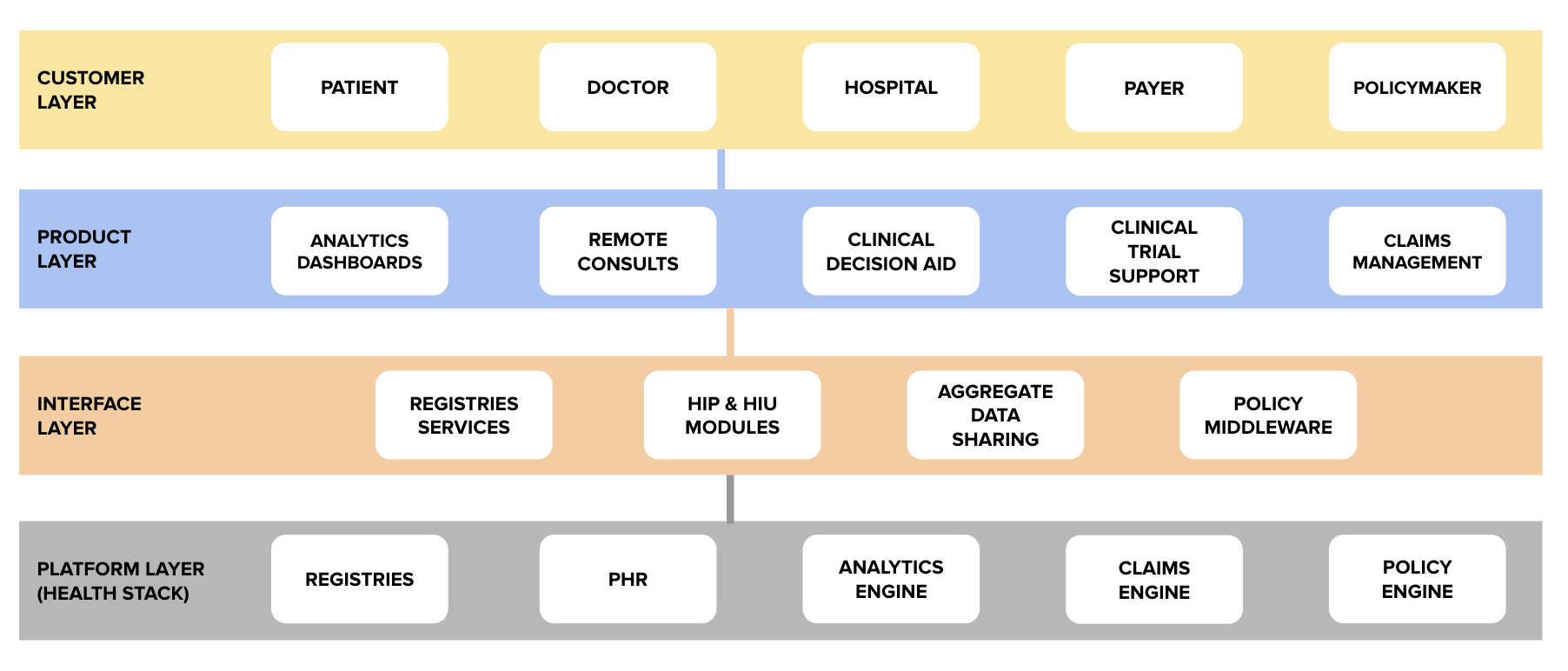
How one entrepreneur’s mountain looks like a VC’s molehill
The apocryphal story of a newbie B2B founder, with deep domain knowledge, but no experience as an entrepreneur or in a startup. Note that while this example is not based on a single entrepreneur, it’s a composite to highlight the extremes.
Amita was a deep domain expert, with 15 years of experience in Wicro’s manufacturing services vertical. She identified a specific problem that a few of her customers had, costing them millions every year, which would get solved with a software product she dreamed about building. Being bitten by the entrepreneurial bug (her classmate founded FlipDeal), she decided to work together with a few old friends and colleagues, and start a business attacking the problem, with a couple of trusting old customers agreeing to do a paid pilot when she had the product ready.
As Amita and her team built the product, they initially used their own savings. Friends advised her to go to VCs, since this was exactly the kind of high-tech manufacturing software product that many VCs said they would fund. Amita was excited, she had seen FlipDeal raise a few Billion $, and felt that though her startup didn’t need as much, it would be good to raise a few million to hasten the pace.
The first VC meeting was a disaster, she was asked for their TAM (Total Addressable Market). And she was hardly able to define it well enough on the fly. The VC also said that manufacturing software was passe, IoT was the future.
“What’s my TAM?” she wondered on the ride back to the office.
“What’s our TAM?” the team asked her.
On the one hand, the specific problem they were solving was only for manufacturers in the auto ancillary business. This was a big sized market they thought, 60 odd large customers and a few hundred smaller ones spread over US, EU. The problem their product solved cost the large companies a few million dollars a year, and cost the smaller companies a hundred thousand dollars a year. Overall solving this problem would save the industry $300M. Of this, they estimated, they could charge $75M for the product.
The team was happy. There were few competitors and they felt they could become a good solid $25M business.
The next meeting with another VC was even worse than the first one.
“$75M TAM for an IoT product? For someone as experienced as you, and with the stellar team you’ve got, why are you taking so much risk — 8/10 startups fail you know — for such a small market?” advised the VC, running a $100M fund. “We will only fund you if you’re looking at a $1 billion market, and can make $100M annual revenue, otherwise the risk/reward doesn’t work out”.
Amita was baffled at how easily she and her team had been about to step into such a bad risk/reward tradeoff, even though they were smart, thorough professionals, who should have known better.
She decided to attack a much larger market, that was nearly the same as what they were trying to solve a problem for. Of course she didn’t know any customer in that area, but they were manufacturers too. Wouldn’t they have the same problems? No one in her team had done sales to the new segment, but how hard could it be to sell to a new vertical?
Back in the office, the team brainstormed the new market, $3 Billion wide, IoT for manufacturing across different verticals. Now the product roadmap had to change, since they needed to address different problems for different verticals, and they needed to make the product more generic. They had to drop some of the more intricate features for the auto-ancillary features too. That market was only a small drop in their overall bucket. So they obviously couldn’t do everything the small little market needed.
Miraculously the next VC agreed to fund Amita’s IoT product startup in a $3B market, and the team was now flush with cash, $2.5M to be exact. “Off to the races, let’s hire more people, build the product, get some more early customers” Amita thought.
But soon things weren’t rosy any more. Building the generic product that spanned multiple markets took much longer than expected.
Their early believers in the auto-ancillary turned sour, the product they were building was now not solving the specific point problem they had.
Their small initial pipeline ran dry, but they had a large pipeline of new prospects who they had never met before, who were all looking good to start engaging. But the sales cycles turned out to be much longer than expected outside of auto-ancillary. Perhaps the problem wasn’t as serious for others?
Their money was running out too, the $2.5M was designed to run for 18 months. Now at 12 months, staring at 6m of runway, with no product launched, no pilots won, and increasingly long sales cycles, Amita was at a loss.
Where had they gone wrong?
Wasn’t it supposed to be less risky to go after a large market?
Shouldn’t they get a great pipeline from the new sales guy they hired for a lot of $?
When their product built for a $75M TAM generated solid early paid pilots, why were they struggling to get any engagement in a $3B market?
Wasn’t it validation that they had a world class VC on board?
_________________
This is the story of some of the most capable founders with deep domain expertise, that I meet every month. While they have tons of deep experience, product ability, and network, it’s typically in a small specific domain, and not in a large, deep market.
In the process of building their startup, IF they move from small markets they know like the back of their palms, to large markets where they don’t know as much, the risk they are taking explodes.
On the other hand, if they are domain experts in the larger market, or end up creating a new large market, out of the small market they start in, then they have a great chance of building a true $1B+ business. Deep domain experts with 20+ yrs of expertise, selling and building for F500 — are best off hunting Whales, or Brontosaurus as Christoph Janz writes.
Typical VC fund economics
VCs with $100M funds need to return $300M to their investors. That’s the promise they make to their investors, 4X gross returns in 10 years as Fred Wilson shows, from a portfolio of top notch startups. And as Tomer Dean points out 95% of VCs fail to deliver sufficient returns to their investors!
So with 8/10 funded startups failing, a VC needs each startup in the portfolio to shoot for a $100M cash return to the fund. With a 20% ownership at exit, the startup must be worth $500M at exit, in 7–10 years from funding.
A startup seeking VC funds, therefore needs to rocket from $5M-$500M market cap in 10 years or less to be a success for a VC. To do this you have to build a $100M revenue business. This demands a market size well in excess of $1B.
At this return rate, the VC is ok if 90% of their startups fail the test, and fall short of returning $100M cash to the fund. That’s the risk/reward the VC is talking about.
At the other end, for a founder who has initial customers, has solved similar problems in the past, has a strong team, there’s actually little risk in making the first $1M revenue. Factor in a small market where no one else is solving the particular problem really well, they have little competition, and may win customers through referrals quickly. They have a good chance at building a $10M revenue startup, which might be valued at $40M.
Computing the risk/reward expected outcomes
In the VC model, going after a large market, the founders/employees end up owning 20% of the company at exit, with a 10% chance of getting there.
20% x $500M x 10% = $10M expected outcome.
In the bootstrapped model, going after a small market, the founders/employees own 80% at exit, with a 40% chance of getting there.
80% x $40M x 40% = $12.8M expected outcome.
Very similar expected outcomes, but very different risk profiles.
On the one hand, VC money is like strapping a nuclear fuel powered jet packon your back. When it works you get to orbit, but 8/10 times when you’re not ready for it, you’ll die.
On the other hand a longer slower more arduous climb up Mt. Everest, the rate of death is still high, but substantially more manageable risk wise.
Which path you choose as a founder, should depend on the size of the market you’re chasing, the cost of acquiring customers in that market, whether there are network effects that aid early movers, how much it will cost to build the product out to the quality the market demands, your own affordable loss, and more. And as Clement Vouillon says both paths are fine, but do know which path you’re on!
Too many founders are going to VCs with sub-scale markets (< $1B), and blaming them for not taking risks. A VC is NOT in the job of taking risks. They’re in job of building a high reward portfolio, and a small market can’t give a high enough reward.
Many founders think this is a one-time decision. Absolutely not! As Atlassian, Github and others have shown, it’s totally possible to bootstrap to find the right market-fit, and then take growth capital when you’re truly ready.
If you’re an early stage SaaS founder, and want to do this better, stay tuned for some hands-on assistance to grow past this choice.
Thanks to Manoj Menon for reading an early draft.