Digitising India is the only sure-shot way to reach the benefit of growth to India’s masses and that then will create the multiplier to ensure the target 8 to 10% sustained GDP growth… [Digital India is] certainly the most appropriate call for transforming India into a vibrant and strong global economy.
– Pramod Saxena, Chairman & MD, Oxigen Services.
And we agree. Digital India has the potential to become one of the most meaningful reforms for Indian businesses in recent history.
As we’ve mentioned in the past, India can fulfill the promise of reaching a double-digit growth for businesses in the near future. But, as the Doing Business reports keep not-so-subtly pointing out, our infrastructure moves like a burdened elephant, rather than a ferocious tiger.
If we want to compete with the swift eagle (U.S) & the nimble dragon (China),we need to adopt tech-savvy practices which help us speed up business in every way – like digital signature certificates to attest the soft copies of documents & invoices. Yet, for many business owners, such practices are either too time-consuming to implement, or have little accessible information about their benefits for them to be understood well.
This is where Digital India can help. Last time, we had a chat about the DigiLocker service, and its possible benefits to Indian SMBs.
This next service which we address today birthed from a realization that digitally signing documents is an important basic amenity in the 21st century. But, it can’t be scaled if the plan calls for a billion people to be provided their own USB pen drive – which is what was required with the Digital Security Certificate system.
This week, let’s talk about eSigning.
This article will answer the following questions:
- How does eSigning work?
- How does it differ from regular Digital Security Certificates (DSCs)?
We will continue our conversation on how this impacts businesses in India in the next article of this week.
What Is eSigning?
Before we get into the ‘how’, we need to clear the ‘what’. And no – eSigning is not the same as getting a digital signature from a government-approved authority.
An eSign is an electronic signature which requires no prior paperwork, as long as you’re a registered Aadhar user. It can be instantly applied for, and approved for, a single-use validity of half an hour.
This differs from an issued long-term Digital Signature Certificate,which has a validity of one to three years, and is usually carried around in a dedicated USB device.
If you’re a user of eSign, this is how the process will seem to you:
- You sit at a regular computer terminal, or a specific one installed by the service provider if you want to provide biometric data.
- You verify your biometrics through the hardware installed by the provider, or through a One-Time Password (OTP).
- You instantly receive a single-use eSignature to affix to whichever document you wish, as long as you use it within the next half an hour.
- That’s it. You’re done. No, we’re not kidding.
Unlike the usual use of the term ‘eSigning’, however, the eSignature services launched under the Digital India campaign do not refer to a traced, handwritten signature on a digital screen or pad.
Instead, these eSignatures are highly regulated, legally binding, valid identity proxies which are issued only after the confirmation of biometric data such as fingerprints or iris scans, or through OTPs sent to the mobile number registered to the user’s Aadhar card.
Of course, there’s a lot more which goes on behind the scenes.
How eSigning Works

The biggest advantage of eSigning as a technological tool is that it’s absurdly simple to use for the end-consumer. However, since it’s a highly regulated service, the behind-the-scenes machinations are significantly more complex.
In the beginning, the architecture of the system is heavily derived from the Application Service Provider (ASP) which is choosing to provide this service to its users. One example of such a service is eMudhra’s emLocker service, which is currently allowing its users to eSign their documents. Another is the Indian government’s DigiLocker.
When a user accesses the eSignature service, the ASP creates the application interface – which acts like an application form. This API is used to access a partner eSign Service Provider (ESP), which is a government-approved entity that is registered as an eKYC authentication user under the UIDAI.
When this connection is established, the user provides an authentication of their identity based on the information saved under their Aadhar profile – either through fingerprint or iris scans, or through an OTP verification code sent to the mobile registered to their Aadhar. As soon as this information matches the saved KYC information in the Indian government’s database, a Certifying Authority – another government-regulated and approved entity –issues a temporary Digital Signature Certificate (DSC). In cases of entities like eMudhra, the Certifying Authority may also be an ESP.
A key pair is generated for that DSC, and an audit trail containing the authentication response and timestamp are created. The ASP finally receives the eSignature from the ESP, which can then be attached to the document. Once received, the user can now fix the signature to the document, and the key is then automatically destroyed after a one-time use.
What Does This Mean For The Future? In Closing
What this means for the future, Ladies & Gentlemen, is rather simple. Imagine a future India where the small-time farmer can self-attest documents online to receive faster access to government services and programs, or where his buyers sign and return invoices online to speed up his receivables due.
Imagine a future where, instead of having to attest twenty copies in thirty different departments when setting up a business, small-time entrepreneurs can simply save their documents on DigiLocker and attest them using eSign services – thus saving them days’ worth of physically running around, eventually helping them set up faster.
Imagine a future where a mistyped document submitted for a business visa would no longer require another appointment and a day at the relevant authorities. Instead, you self-attest the correct document online and send them a link.
Or an India where eInvoicing becomes the norm, like so many developed and developing countries in the world. Psst, by the way, eInvoicing can help cut as many as five days from the invoicing process, and so get you paid much faster. But more on that later.
Getting back to the point, that India isn’t so far ahead in the future. In fact, with eSigning and Digital Locker integration within services such as emLocker and DigiLocker, that India is already at our doorstep.
But then, we are but one voice. How helpful do you believe eSigning to be in the larger picture? Let us know in the comments section below.
with Inputs from Aniket Saksena

 The policy changes announced by RBI are as follows:
The policy changes announced by RBI are as follows: Lastly, while the RBI has positively stated that it will notify certain changes soon, all of MCA issues and a majority of RBI issues are still at a ‘discussion/recommendation stage’ (and have been merely acknowledged by the authorities as issues that need to be resolved). Hopefully, the authorities will not stop here, and will implement all these changes soon. Needless to add, iSPIRT will keep interacting with, and assisting, the authorities in achieving a quick closure to these items, as well as the remaining issues which have not yet been touched by the authorities.
Lastly, while the RBI has positively stated that it will notify certain changes soon, all of MCA issues and a majority of RBI issues are still at a ‘discussion/recommendation stage’ (and have been merely acknowledged by the authorities as issues that need to be resolved). Hopefully, the authorities will not stop here, and will implement all these changes soon. Needless to add, iSPIRT will keep interacting with, and assisting, the authorities in achieving a quick closure to these items, as well as the remaining issues which have not yet been touched by the authorities.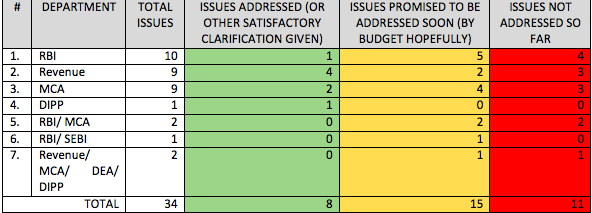
 What are some of the learning’s from this effort?
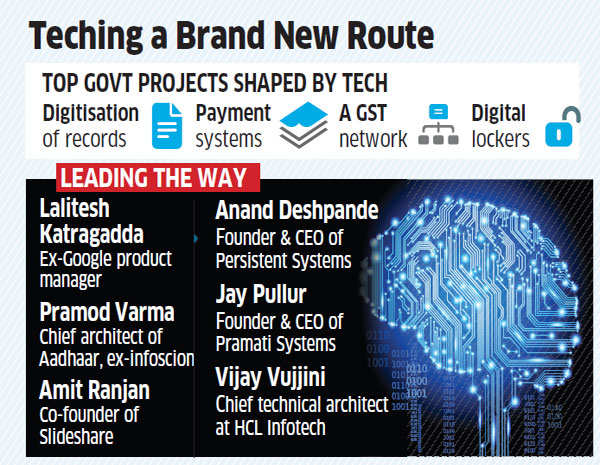
What are some of the learning’s from this effort? The first session was about understanding the technology trends that are shaping banking. There was special focus on understanding implications of eKYC, Aadhaar, new payment infrastructure and GST Network. There was also a good discussion how point-solutions by startups are changing banking.
The first session was about understanding the technology trends that are shaping banking. There was special focus on understanding implications of eKYC, Aadhaar, new payment infrastructure and GST Network. There was also a good discussion how point-solutions by startups are changing banking. iSPIRT is fostering many such dialogs with not just banking giants like
iSPIRT is fostering many such dialogs with not just banking giants like  Efforts of iSPIRT’s List-in-India Policy Expert Team have reaped the desired results. The securities market regulator, SEBI, has announced relaxed norms for a separate platform to allow “new-age companies” having an innovative business model and belonging to the knowledge-based technology sector to list in the country.
Efforts of iSPIRT’s List-in-India Policy Expert Team have reaped the desired results. The securities market regulator, SEBI, has announced relaxed norms for a separate platform to allow “new-age companies” having an innovative business model and belonging to the knowledge-based technology sector to list in the country. What was so Infectious? Its the Mirror Neurons, Stupid!
What was so Infectious? Its the Mirror Neurons, Stupid!  What is the Cure? More Infection. Make India Go Cashless.
What is the Cure? More Infection. Make India Go Cashless. Conclusion
Conclusion Our Open API effort is based on some core principles:
Our Open API effort is based on some core principles: